What is a Binary Heap in Python?A binary heap is one of the important non-linear data structures in Python. A heap is a complete tree. Heaps are an efficient implementation of a data structure called the priority queue. W. J. Williams introduced a binary heap in 1964, whose main purpose was implementing the heap sort algorithm. A heap is not an ordered data structure. Binary heaps can be of two types:
Identifying if a binary tree is a heap:
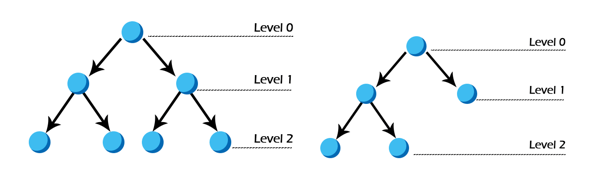 The above two binary trees are heaps.
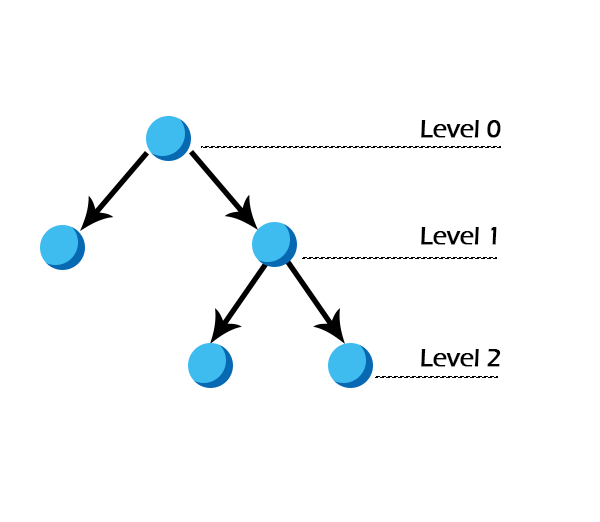 In this binary tree, in the second last layer, i.e., layer 1, only 1 node is filled, but the leaf nodes to level 1 are not filled from left to right. Hence, it is not a heap. In this tutorial, we'll learn about a Min heap with examples. Notable applications of Heap data structure:
Representation:A binary heap can be represented using arrays like a binary tree:
To place all the other nodes into the array, there are two formulae to use and one to verify:
Verification: Parent index = (child index - 1)/2 Here is an example: Now, let us create an array to represent the heap: 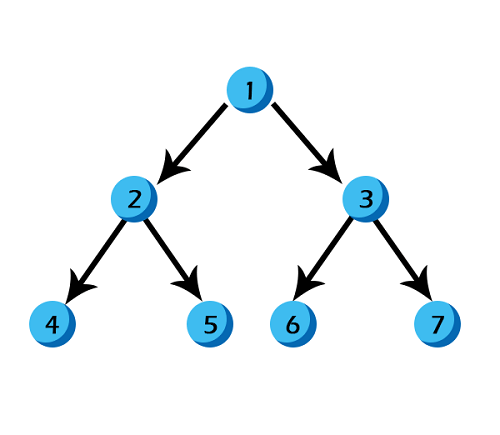 1. The heap has 7 nodes. Hence, we need to create an array of length 7: (0-6) 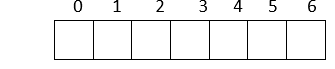 2. The root node in the heap is 1. Place 1 at index 0 in the array 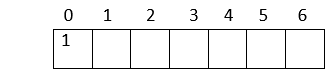 3. Now, looking at the left child for 2: Left child = 2*index of its parent in the array + 1 = 2*0 + 1 = 1 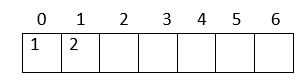 4. Right child of the root node: 3 Right child = 2* index of its parent in the array + 2 = 2*0 + 2 = 2 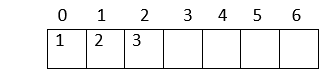 5. In the next level: child nodes of node(2) 4: Left child = 2*index of its parent in the array + 1 = 2*index(2) + 1 = 2*1 + 1 = 3 5: Right child = 2* index of its parent in the array + 2 = 2*index(2) + 2 = 2*1 + 2 = 4 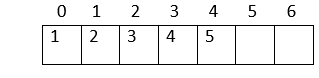 6. Child nodes of node(3): 6: Left child = 2*index of its parent in the array + 1 = 2*index(3) + 1 = 2*2 + 1 = 5 7: Right child = 2* index of its parent in the array + 2 = 2*index(3) + 2 = 2*2 + 2 = 6 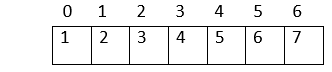 Hence, the above heap is represented as an array: Operations on a heap:1. Heapify: Given a binary tree, converting it into a heap is called "Heapify". We use the array implementation of the tree, and we'll convert it into an array representing a heap: Output: [1, 2, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5] As you can observe, the minimum node 1 is kept at the root(index-0) position, satisfying the minheap property. 2. Inserting a node Given a node, we need to append the node to the array at the end such that the last node from left to right is getting filled, and the most important step is to heapify the array after insertion: Output: [2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 5] [1, 3, 2, 6, 7, 5, 4] We inserted 1 into the heap. Among all the elements in a heap, 1 is the smallest; according to the minheap's property, it must be placed at the root(index-0). 3. Deleting elements from a heap If the node we want to delete from the heap is a leaf node, we can delete it. If it is an internal node, we need to swap the node with any leaf node and then delete it.
Output: [2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 5] [1, 3, 2, 6, 7, 5, 4] [2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 5] 4. Get Minimum node/ Maximum node: In a minheap, the root node will have the minimum value. Hence, we can write a function to find the min node and return the root(index-0). In the same way, in a maxheap, the root node will have the maximum value: Output: 3 Heapq Module:As discussed earlier, we can implement a priority queue using a heap. In the libraries of Python, there is a module - The heapq module meant for implementing the priority queue algorithm. The module consists of functions for different heap operations like: 1. heappush(heap, node) To insert a node into the heap 2. heappop(heap) The function deletes and returns the smallest element in a heap. 3. heapify(list) Converts the given list into a heap in linear time We'll now try to implement the heap operations-insertion and deletion using the heapq module: Output: Heap: [1, 2, 4, 3, 6, 5] After deleting element at 0th index: [2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Minimum node: 2 Heapsort:Heapsort is one of the sorting algorithms available. To sort the elements, we'll push all the given values into the heap, and after all the elements are inserted, we'll keep popping the smallest elements one at a time, one after the other: Output: [1, 2, 3] Next TopicWhat is a Namespace and scope in Python |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










