Simple To-Do List GUI Application in PythonThere is a set of tasks that awaits us every new day. Some of them might be interesting, and some can be tedious. However, the significance of completing these tasks is unquestionable, specifically in case they build on a regular basis. There might be times when many of us struggle to keep a record of what we require. Perhaps some of us are in the habit of using a handwritten to-do list to remind ourselves of the pending things and their deadlines. However, handwritten notes have a higher chance of getting lost or forgotten. Since we are the Python coders, it makes sense to build a To-do list manager GUI application using Tkinter. In the following tutorial, we will see the step-by-step procedure to build a simple To-Do list manager GUI application using the Tkinter library in the Python programming language. But before we start, let us briefly understand what a To-Do list is and its benefits. What is a To-Do list?A To-Do list is a list of tasks we require to complete or things we would like to do. Most typically, the tasks in this list are arranged in order of priority. By tradition, they are written on a piece of paper or post-it notes and act as a memory aid. Due to the evolution in technology, we have been able to create a To-Do lists with Excel Spreadsheets, Word Documents, E-mail Lists, and To-Do List applications like Microsoft to-do and Google to-do lists. We can utilize a to-do list in our home, workplace, or personal life. Having a list of everything we are supposed to do written down in one place implies that we should not forget anything significant. By prioritizing the tasks in the list, we can play the order of doing them and quickly observe what requires our immediate attention and what tasks can be delayed for a while. Understanding the Advantages of using a To-Do ListOne of the significant reasons to use a to-do list is that it will support us in staying planned. Whenever we write all the tasks in a list, they appear more convenient. When we have a clear outline of the tasks that require action and those we have completed, it supports us in staying concentrated. At the same time, releasing the space in our minds for other, more creative tasks. When we finish a task, we can either mark it down or cross it off the list. This provides us with a sense of progress and achievement, something we will lack if we always rush from one task to the next. If we feel a sense of achievement, it spurs us on and motivates us to keep moving. However, that's not the only advantage of a To-Do list. Some of the advantages of using a To-Do list are shown below:
Now that we have learned about the To-Do lists and their benefits, it is time to start building a To-Do list application to manage our day-to-day tasks. Building a To-Do list application using TkinterThe procedure of building a To-Do list management application using Tkinter is divided into several steps. These steps are shown below: Step 1: First, we will import all the modules required to build the project. Step 2: We will then define some functions necessary to execute the application. Step 3: We will then create a main window for the application. Step 4: We will then add a database to the application to store the data. Step 5: We will add the necessary widgets to the application and apply the event triggers. Step 6: Calling the functions in the main function of the application. Let us discuss these steps in detail. Importing the required modulesBefore we start building our projects, it is important to import the modules necessary for the working of the application. We will import all the required widgets and modules from the Tkinter library to provide the Graphical User Interface touch to the application. We will also import the sqlite3 module to store the data in a database. Let us now consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we have imported the tkinter module as tk. We then imported the ttk module and the messagebox from the Tkinter library. At last, we have imported the sqlite3 module as sql. Defining the functions for the applicationOnce we have successfully imported the required modules, it is time for us to define various functions to operate different events in the application. These functions will allow us to add a task to the list, delete a task from the list, delete all the tasks from the list, update the list, clear the list, retrieve the database, and close the application. We will start by defining an empty list that will help us store the tasks. The following is the snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: We have defined an empty list as tasks in the above code snippet. This list will allow us to store all the tasks entered. Let us now define all the functions necessary for the execution of the application. Adding a Task to the listThe first function we will define for the application will be to add a task to the list. This function will retrieve the string containing the task from the entry field and store it in the list and the database. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the definition of such a function. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as add_task. We have used the get() method to retrieve the string from the entry field and stored it in the task_string variable. We then check whether the string is empty. If the length of the task_string variable is zero, a message box will be displayed showing the 'Field is Empty' message. In case the string is not empty, we have used the append() method to add this string to the list we created earlier. We have also used the execute() method to execute the SQL statement 'insert into tasks values (?)' and stored the value present in the task_string in the database. We have then called the list_update() function to update the list and deleted the entry in the entry field with the help of the delete() method. Updating the listWe will now define another function that will allow us to update the list and insert the entries in the list box. Let us consider the following snippet of code illustrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined a function as list_update. Within this function, we have called the clear_list() function to clear the list. We then used the for-loop to iterate through the tasks in the list and the insert() method to insert the tasks in the list box. Deleting a task from the listWe will now define a function to delete the selected task from the list and database. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined the function as delete_task. Within this function, we have used the try-except method to get the selected entry from the list box using the get() method and store it in the the_value variable. We then checked the selected value in the tasks list and removed it from the list. We have then called the list_update() function to update the list and used the execute() method to execute the SQL statement 'delete from tasks where title = ?' and delete the value from the the_value variable. We have also displayed the message box with the 'No Task Selected' message for an exception. Deleting all the entries from the listWe will now define a function that will delete all the tasks from the list. Let us now consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we have defined a function as delete_all_tasks. Within this function, we have displayed a message box to ask the user for their confirmation. We have then used the if conditional statement to check if the value is True. We have then used the while loop to iterate through the elements of the tasks list and pop them out with the help of the pop() method. We have then used the execute() method to execute the SQL statement 'delete from tasks'. At last, we have called the list_update() function to update the list. Clearing the listWe will now define a function to clear the list. The following snippet of code illustrates the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we have defined a function as clear_list. Within this function, we have used the delete() method to delete all the entries from the list box. Closing the applicationWe will now define a function to close the application. We will also print the final list in Command Prompt. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we have defined a function as close. Within this function, we have printed the tasks list for the users. We have then used destroy() method to close the application. Retrieve data from the databaseWe will now define a function to retrieve data from the database and append the values to the list. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we have defined a function as retrieve_database. Within this function, we have used the while loop to iterate through the elements in the tasks list and pop them out with the help of the pop() method. We then used the for-loop to iterate through the rows in the database table and used the append() method to insert the values from the table to the list. Creating the main window for the applicationNow that we have defined all the necessary functions for the application, it is time for us to design the main window for the application where all the widgets will be displayed. This can be done by creating an object of the Tk() class of the Tkinter library. Let us now consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we have created an object of the Tk() class of the Tkinter library. We have then set the title of the window using the title() method. We have then used the geometry() method to set the size and position of the window. We have also disabled the resizable option for better UI by setting the parameters of the resizable() method to zeros. At last, we have used the configure() method and set the background color of the window to #FAEBD7. Adding the database to the applicationWe will now add the database to the application, which will store the data for the user. We will start using the connect() method to connect to the database. We will then create an object of the cursor class, which will allow us to execute SQLite statements and fetch data from the result sets of the queries. We will then use the execute() method to execute the SQL statement. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we used the connect() method. We have then created an object of the cursor class. We have then used the execute() method to execute the SQL statement 'create table if not exists tasks (title text)'. Adding the necessary widgets to the application and applying event triggersNow that we have successfully added a database to the application, it is time to add necessary widgets to the main window and apply the essential event triggers. We will start by adding frames to the main window. These frames will provide a proper structure to other widgets. We will then add some labels to these frames to provide some information. We will then add an entry field so the user can enter their task. We will also add some buttons that perform specific functions like adding a task to the list, deleting one task from the list, deleting all tasks from the list, and closing the application when clicked. We will also add a list box to display all the entered tasks. Let us now understand the implementation of the same in detail. FramesFirst, we will add frames to the application using the Frame() widget of the tkinter module. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the implementation of the Frame() widget. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Frame() widget to define some frames for the application. We have set the master parameter of these widgets to guiWindow, the object of the Tk() class and the bg parameter specifying the background color to "#FAEBD7". We have then used the pack() method to place these frames in the application. LabelsWe will now add the labels to these frames using the Label() widget of the ttk module of the Tkinter library. These labels will represent the application's heading and the entry field's title. Let us understand the implementation of the labels in the following snippet of code. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have used the Label() widget of the ttk module to define a label setting its master parameter to header_frame, a frame we defined earlier. We have also set the text, font style and size, background, and foreground color. We have then used the pack() method and set the position of this label on the window. We have then defined another label using the Label() widget of ttk module and set its master parameter to functions_frame, another frame we defined earlier. We have again set the text, font style and size, background, and foreground color. We have then used the place() method to set the position of this label on the main window. Entry FieldWe will now add an entry field to the application using the Entry() widget of the ttk module of the Tkinter library. This entry field will allow us to insert the task title in the list. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the implementation of the Entry() widget. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined an entry field using the Entry() widget of the ttk module and set the master parameter of this widget to functions_frame, a frame we defined earlier. We have also set the font style and size along with the width of the widget. We have also set the background and foreground color of the entry field. We have then used the place() method to place this entry field in the application. ButtonsNow it is time for us to add some buttons to the application to perform certain functions we defined earlier. We can create these buttons using the Button() widget of the ttk module of the Tkinter library. The following is the snippet of code illustrating the creation of the buttons. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code, we have defined some buttons using the Button() widget of the ttk module. We have set their master parameters to functions_frame, a frame we defined earlier. We have also set the text these buttons will display along with the width of each button. We have then set the value of the command parameter to the functions they will call. We have then used the place() method and set their positions on the main window. List boxWe will now add a list box to the application using the Listbox() widget of the tkinter library. This list box will display the list of tasks. Let us consider the following snippet of code illustrating the implementation of a list box. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above code snippet, we used the Listbox() widget of the tkinter module. We have set the master parameter of this widget to listbox_frame, a frame we defined earlier. We have set the width and height of the list box. We have also set the selectmode parameter to SINGLE so that entry will be selected once at a time. We have then set the background and foreground color and background and foreground color of the selected entity. We have then used the place() method to place the list box in the application. Calling the functionsWe will now call the functions to retrieve the database and update the list. We will also use the mainloop() method to run the application and establish the connection with the database. Let us consider the following snippet of code demonstrating the same. File: todo_application.py Explanation: In the above snippet of code we have called the retrieve_database() function along with the list_update() function. We have then used the mainloop() method with guiWindow, an object of the Tk() class, to run the application. We have then established the connection with the database using the commit() method and close() method. Hence, the project code is now completed. We can save the file and run the following command in a command shell or terminal to see the output. Syntax: Before we see the output, let us consider the complete code of the "To-do List GUI Application" project in Python. The Complete Project CodeThe following is the snippet of code of the " To-do List GUI Application" project in the Python programming language. File: todo_application.py Output: ['Exercise', 'Practice Coding', 'Complete Assignment', 'Shopping'] 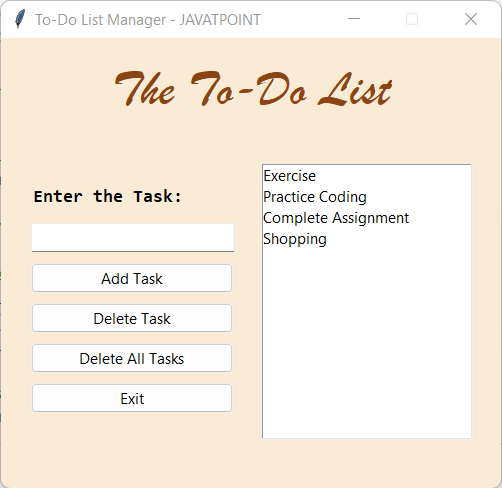 Next TopicAutomate Software Testing with Python |