Python Variance FunctionWe can utilize the statistics package's powerful capabilities to calculate any statistic-related task. One of these functions is variance(). We can calculate the data sample's variance with this method's aid (the sample is a small part of population data). We can use the variance() function when calculating a sample's variance. The variance of the total population can be determined using a different function called pvariance(). The square of the deviation of a quantity from its mean is known as variance in elementary statistics. In essence, it assesses how far random data from the data mean, or median score is spread apart. While a high number would suggest that the supplied set of data is much more split out from the average value, a lower score for a variance would suggest that the data values are grouped around the mean instead of spreading apart. In science, wherein statistical data analysis is widespread, variance is a crucial tool. It is also referred to as the given data's second central moment and is equal to the square of the dataset's standard deviation. In pure statistics, it is typically expressed as s2, σ2, and Var(). Mathematically variance is the result of the squared mean of the deviation of the individual data points from the mean. 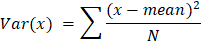 Syntax of the variance function Parameters
Return type: This function returns the variance of the dataset given to it. Example - 1Code Output: The variance of the data sample is:- 0.6397066666666666 Example - 2Code Output: Variance of the Sample_1 is:- 5.238095238095238 Variance of the Sample_2 is:- 3.7666666666666666 Variance of the Sample_3 is:- 61.714285714285715 Variance of the Sample_4 is:- 2549/17280 Variance of the Sample_5 is:- 0.52253 Example - 3Code Output: The variance of the data sample is:- 20.435000000000002 Example - 4We'll now see that the variance value becomes incorrect if the xbar parameter's value differs from the actual mean or average value. Code Output: The mean of the sample set is:- 2.5 The correct variance of the sample set is:- 20.435000000000002 The incorrect variance of the sample set is:- 11839.96625 Example - 5We will see how to when the variance() function will raise the StatisticsError. Code Output: StatisticsError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-5-d7f3060a7f32> in <module>
8
9 # Passing an empty dataset to the function will raise the StatisticsError
---> 10 print(statistics.variance(sample))
/usr/lib/python3.8/statistics.py in variance(data, xbar)
739 n = len(data)
740 if n < 2:
--> 741 raise StatisticsError('variance requires at least two data points')
742 T, ss = _ss(data, xbar)
743 return _convert(ss/(n-1), T)
StatisticsError: variance requires at least two data points
Applications of Calculating VarianceVariance is a crucial technique for processing massive quantities of data in statistics. For instance, variance is employed as a biased estimator if the sample mean value (the correct mean) is unknown. Only a limited number of real-life observations may be made, such as the value changes of all corporation stocks during the day. As a result, variance is computed from a limited collection of data; even if it doesn't match when computed with the entire population in mind, it will still provide the user with an estimate sufficient to plan further calculations. |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










