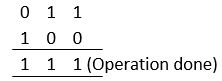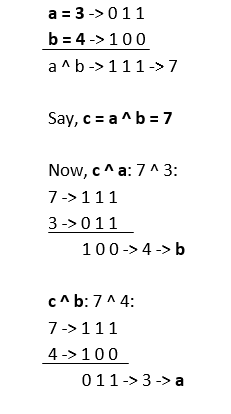Python Bitwise XOR OperatorBinary language is the language of a computer. All the inner mechanisms of a computer happen concerning bits. Bitwise operators are the set of operators that allow the programmer to perform bitwise operations on integers. These operators allow the programmer to manipulate the lower-level data in a computer. There are a total of six bitwise operators in Python: - Bitwise AND
- Bitwise OR
- Bitwise NOT
- Bitwise XOR
- Bitwise right shift
- Bitwise left shift
This article discusses the Bitwise XOR operator with examples. - When we apply a bitwise operator on two operands, the integer values are converted into their binary forms-into bits.
- Then, the operator performs the operation bit-by-bit on every individual bit.
- After the operation, the binary number is converted to decimal form and returned as the output.
Now, let us understand the operation of Bitwise XOR: - It is called "Exclusive OR". It excludes the 1 | 1 -> 1 condition from 'or'.
- It is a binary operator - performed between two operands.
- Representation: a ^ b where 'a' and 'b' are two operands.
- Return value: It returns an integer when performed between two integers and a Boolean value when performed between two Boolean values.
Operation: - The given two integers are converted into binary form.
- In the two binary notations:
- If both corresponding bits are the same - (1 ^ 1), (0 ^ 0), it returns 0.
- If both corresponding bits are different - (1 ^ 0), (0 ^ 1), it returns 1.
After xor is performed on all the bits, the resultant binary number is converted back to decimal and returned.The truth table of XOR: | Bit 1 (operand 1) | Bit 2 (operand 2) | Return value |
|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 1 | 0 | 1 | | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Let us understand the concept using an example: If we want to perform: 3 ^ 4: 1. Both the integers are converted into binary forms: 3 -> 0 1 1 4 -> 1 0 0 2. Now, xor is applied bitwise: 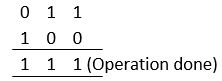 3. Finally, the resultant binary number is converted back to its decimal form. 1 1 1 represents 7 4. Output -> 7 3 ^ 4 -> 7 Now, for the same operands, let us write a code for xor: Output: 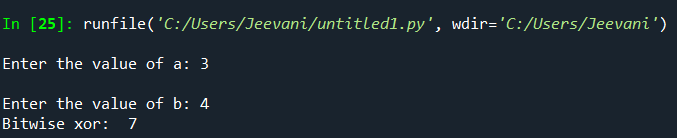 On Boolean values:We can perform xor on Boolean values. When we operate on two integers, 1 is equivalent to Boolean True, and 0 is equivalent to Boolean False. Truth table: | Operand 1 | Operand 2 | Operand 1 ^ Operand 2 |
|---|
| True | True | False | | False | False | False | | True | False | True | | False | True | True |
Output: 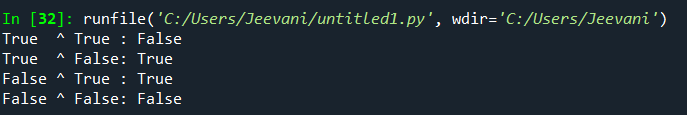 Structure of outputs: - If we performed xor on a and b -> a ^ b. As a result, we got some integer c (a ^ b -> c) then,
- If we perform xor on c and a, b will be the output -> c ^ a -> b
- If we perform xor on c and b, a will be the output -> c ^ b -> a
Let us take the above example: 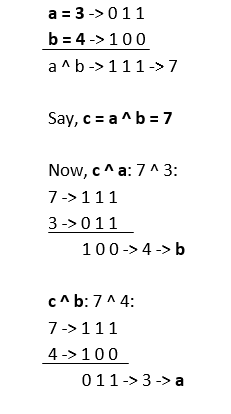 Code: Output: 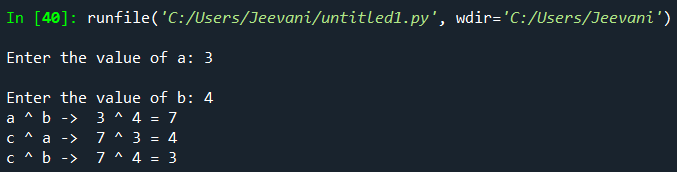 Understanding: If a ^ b -> c Then, c ^ a -> b c ^ b -> a - If we know the output and one operand, we can find the other operand using this relation.
- This relation is only possible with xor because of its truth table.
Role of xor in cryptography:The above relation got xor a small role in cryptography models. - If a person 'A' wants to send a numerically encoded message to another person 'B' confidentially, he needs one more simple cover for the encoded message.
- Both A and B will have a secret key known to each other beforehand.
- Now, A will XOR the message with the secret key and send it to B.
- After receiving, B can perform xor again with the received xor result and secret key and get the message.
Example: If A wants to send the message 3 to B and their secret key is 4 3 ^ 4 -> 5. A will send 5 to B. B already knows the secret key is 4. He will decrypt the message using xor again: 5 ^ 4 -> 3 Message successfully received. - This method is the simplest, and so is the weakest cryptography method.
|