os.path.abspath() method in PythonWhat is OS Module?In the Python programming language, we have an OS module which is used for the various operations related to the operating system. It has a lot of inbuilt functions, and we do not have to install this module. The path is the submodule in the OS module, which contains some inbuilt functions related to the operations on path names of any file or folder present in our computer. For Example:os.path.dirname(path) It is supposed to return the directory name of the path which we have provided as the argument of the function. os.path.basename(path) This function is supposed to return the base name of the path given as a parameter in the function. os.path.commonprefix(listOfPaths) This function is supposed to return the common prefix present in all the paths of the given list. If there is no common prefix then it will give an empty string as output. os.path.exists(path) This function returns a Boolean value. If the given path exists in our system then it will return a value as true otherwise, it will give a value as false. os.path.lexists(path) This function returns true for broken symbols of an existing path. os.path.getatime(path) It returns some floating number which represents the number of seconds before we access the file which we provided in our path as the function argument. If the file does not exist then it will give the error. os.path.getmtime(path) It returns some floating number which represents the number of seconds before we modify the file which we have provided in our path as the function argument. If the file does not exist then it will give the error. os.path.getsize(path) It returns the size of the file in bytes. If the file does not exist then it will throw the error. os.path.splitdrive(path) This function splits the path into two parts which we pass as an argument. The two parts are the drive part and the tail part. Drive parts denote the drive in which or path exists, like C: drive or D: drive etc.Tail part is the remaining part of the path of the file. os.path.samefile(path1,path2) This function is supposed to return true if path1 and path2 refer to the same file or directory, which are passed as an argument of the function. If path1 and path2 denote different files or directories then it will return false. os.path.splitext(path) This function is supposed to split the given path into two parts: the first part is the root and the second is the extension. In the path name, all the strings and characters before the period(.) are the root part, and after the period(.), it is an extension, including the period. If there is no extension then the second part will be empty. os.path.abspath(path) This function takes the path as an argument, and it returns the normalized pathname of the given path. It returns the complete path of the file in the system. Syntax:Return value:The absolute pathname of the given path Example 1:Output: 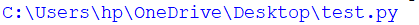 Explanation: In the above code, we have tried to print the absolute path of the given file. Firstly, we have imported the os.path module using the import keyword. Then, we took the file name which is present in the current directory in which we are working. We have given the file name as an argument in os.path.abspath() module, and then we have printed it using the print command. Note: We can change the current working directory, and then also we can use the function.Example 2:Output: 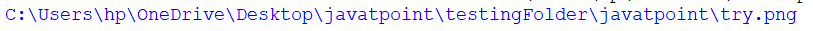 Explanation: In the above code, we have imported the OS module to use its inbuilt required functions in the file. Then we have taken one file name and stored it in one variable. Now, we have changed the current working directory using the function chdir(), which is already defined in the OS module of Python. Now, we have used the function abspath() to get the absolute name of the file. So, if we print the result then we can see that the absolute path has been changed. Next TopicEmerging Advance Python Projects 2022 |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










