Java StringIn Java, string is basically an object that represents sequence of char values. An array of characters works same as Java string. For example: is same as: Java String class provides a lot of methods to perform operations on strings such as compare(), concat(), equals(), split(), length(), replace(), compareTo(), intern(), substring() etc. The java.lang.String class implements Serializable, Comparable and CharSequence interfaces. 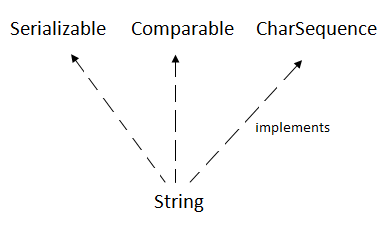 CharSequence InterfaceThe CharSequence interface is used to represent the sequence of characters. String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes implement it. It means, we can create strings in Java by using these three classes. 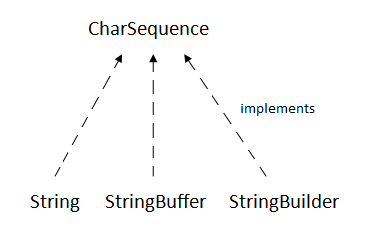 The Java String is immutable which means it cannot be changed. Whenever we change any string, a new instance is created. For mutable strings, you can use StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes. We will discuss immutable string later. Let's first understand what String in Java is and how to create the String object. What is String in Java?Generally, String is a sequence of characters. But in Java, string is an object that represents a sequence of characters. The java.lang.String class is used to create a string object. How to create a string object?There are two ways to create String object:
1) String LiteralJava String literal is created by using double quotes. For Example: Each time you create a string literal, the JVM checks the "string constant pool" first. If the string already exists in the pool, a reference to the pooled instance is returned. If the string doesn't exist in the pool, a new string instance is created and placed in the pool. For example: 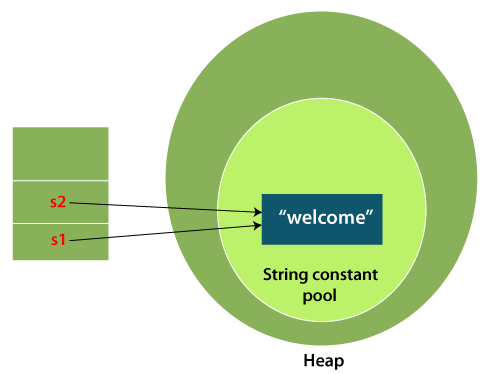 In the above example, only one object will be created. Firstly, JVM will not find any string object with the value "Welcome" in string constant pool that is why it will create a new object. After that it will find the string with the value "Welcome" in the pool, it will not create a new object but will return the reference to the same instance. Note: String objects are stored in a special memory area known as the "string constant pool".Why Java uses the concept of String literal?To make Java more memory efficient (because no new objects are created if it exists already in the string constant pool). 2) By new keywordIn such case, JVM will create a new string object in normal (non-pool) heap memory, and the literal "Welcome" will be placed in the string constant pool. The variable s will refer to the object in a heap (non-pool). Java String ExampleStringExample.java Test it NowOutput: java strings example The above code, converts a char array into a String object. And displays the String objects s1, s2, and s3 on console using println() method. Java String class methodsThe java.lang.String class provides many useful methods to perform operations on sequence of char values.
Next TopicImmutable String |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










