How to Use Redis with PythonThis tutorial will learn how to implement Redis using Python programming language. Redis is a lightning-fast in-memory key value that can be used to store anything. This tutorial will explain the deep understanding of Redis with Python, and we will understand some examples. We will also learn how to connect and use Redis in Python. If you have a basic understanding of Python or Redis, you will easily understand the concepts of Redis. Before diving into this tutorial, let's introduce Redis and why we use it. IntroductionRedis is an acronym for the Remote Dictionary Server, an open-source NoSQL database. It is widely used and famous to be a fast, in-memory key-value data store, message broker, cache, and queue. It was initially developed by Salvatore' antirez' Sanfilippo. Redis has been written in the ANSI C language and works in most POSIX systems, such as BSD and Linux, without any external dependencies. It comes with a wide range of data support such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyper logs and geospatial index with radius queries. Let's have a look at why we use Redis. Redis FeaturesRedis's features are pretty significant and can boost the existing environment with several features. Redis has some essential and beneficial features to be used. Wide Range of Data StructureRedis mainly provides five possible data support: hashes, lists, sets, strings, and sorted sets. Redis stores the data in the key-value pair and offers various data structures to fulfill the application requirements. Data PersistenceData persistence refers to how data survives after the producer process of the particular data has ended. In other words, saved data must be available if the server fails. To ensure data persistency, the data must be stored in non-volatile storage. PerformanceRedis is known for its performance and is highly efficient because of its in-memory nature. Redis's in-memory feature performs well compared to database systems that write every change to disk before considering a transaction committed. High AvailabilityRedis allows us to create and build highly available solutions or clustered topologies. It is primarily a single-threaded server, but the modern version of Redis uses threads for different things. Simply Efficiently and LightweightHence, it is written in ANSI C language and has no dependencies. The program works perfectly well in all the POSIX environments. Redis does not support the Window platform, and Redis also supports various languages such as Node.js, PHP, Ruby, Python, and many others. Redis has tremendous and dynamic community support. CachingCaching makes the Redis faster where data is stored in the temporary storage that can be accessed more quickly in future. Redis provides caching solutions such as images, files, metadata, and persistence session. Installation of Redis on WindowRedis is officially not supported by the window. However, we can set up the Redis in the Window machine by installing the Window Subsystem for Linux 2 and configuring it. To install the window subsystem, you can follow the install Linux on the window with WSL guide. Alternately, we can run Redis on a container using Docker. To do so, we need to install the Docker in the window machine, and we need to download the Docker Desktop from its official site. Once the download is completed, enter the following command in the terminal to fetch the Redis image from the Docker hub. The below command will help to build and run the container. After pressing enter, start a container using the Redis image we downloaded earlier.  Now click on the download button.  As we can see that redis is now running in the system.  Now, we have successfully started the redis server in our system. Install Redis on UbuntuThe first step is to update the repository cache of Ubuntu. We can do it using the following command. Now, enter the following command to install Redis. Now, check the installed version of the installed redis using the following command. The above command will display the installed version of the current utility installed on the system. Now, let's move to the setup of the connection between redis and Python. 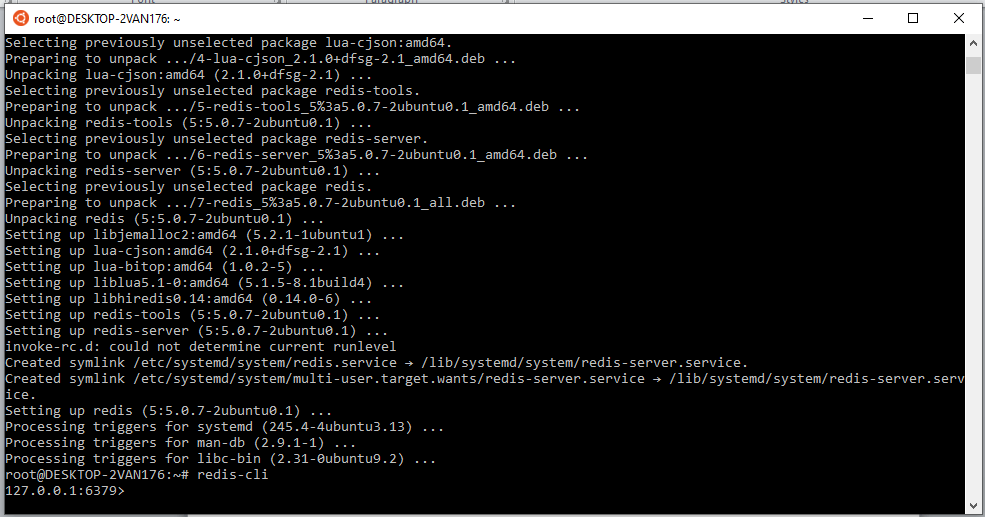 Install Redis-PyTo work with the redis using Python, we need to install the Redis-py library, a Python-Redis client. To open the terminal, run the following command. Redis as Python DictionaryRedis stands for Remote Dictionary Service. We can draw many similarities between the Python dictionary and the working of the redis.
Let's create our first database on the redis, which will be a mapping of the county: capital city, where we use SET to set key-value pairs.  Using Redis-pyTo perform any operation using the redis-py, we need to connect to the redis server, which is very direct in redis-py. We need to decode_response parameter as true so that we do not get the response in bytes format. Let's understand the following example - Example - Now, we have connected to the redis server, we can perform simple CRUD operations. As we discussed earlier, it supports the get, set method. To set the key-value pair, we use the "set" function that takes key and the value as the parameter. Here the point is to remember that, we can only use either of string data types or bytes. Same as the dictionary, we use the get method to get the value of the India. The get function takes the key and return value. The redis module provides the mset method to set the multiple key-value pair. As its name suggest mset - multiple set. Let's see the following example - Output: London The redis module provides the sass function to set a key-value pair where the value is a set data -type. The set data type stores the unique values. To get all the values of fruits that we just stored, we can use the "smembers" function. Now, we will use store the list data types using the lpush function. Let's understand the following example - We use the lrange function to get all the element of the list. It helps us to traverse the elements in the list. We can perform same operations as we perform in the list. Let's see the following example - We can also store the deeply nested objects with different data types; serialization technique like using json or pickle can be used. Let's understand the following example - Example - To extract the information stored, we can directly use "get" function and then undo the stringification performed by json. Output: {'name': 'Megha',
'age': 25,
'address': {'house_no': 189, 'flat_name': 'Golden Flower', 'area': 'Guindy'},
'languages_known': ['english', 'hindi', 'tamil']}
Since it is an in memory data store, it is important that old key-value pairs get deleted or rather expired to make room for storing new data. For this, Redis has the key expiry option available. Let us now try to store a key-value pair with an expiration time. We can make use of the "setex" function to set the expiry for a key-value pair. It accepts the TTL in seconds. If you want to set the TTL in milliseconds, you can use the "psetex" function. Redis Important MethodsThe below table has some crucial commands related to key-value expiration. Let's see the following example.
Using Enterprise Redis ApplicationRedis is an open-source, accessible, and several managed database. It also has additional features built on top of the open-source Redis server.
The designs of the two have some commonalities. ConclusionThis tutorial includes how to implement Redis through Python, including installing and using the Redis REPL connected to the redis server and using redis-py in real time example. We have learned how to activate the Redis CLI through an intuitive Python API. We have learned how to store data in the database. Some of the important concepts of the redis we didn't cover in this tutorial. However, you can go through its official documentation. This tutorial will help you get the good knowledge to embedded Python with redis. |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










