How to Parse JSON in PythonFoundation/ A brief on the pre-requisite knowledge: JSON stands for "JavaScript Object Notation". It is a standard syntactic style used to store in the form of files and exchange data (Interchange) over networks. The syntax of JSON is just simple text, which makes it more high-level. It is derived from JavaScript, but it is language-independent for usage. Data storage is achieved with the use of two types of data structures used in almost all programming languages in one or the other form:
JSON files have an extension.json, and network transfers have a wide range of electronics and digital systems applications. The programmer has to parse the data into some programming language to work with the human-readable data inside the JSON files. There are inbuilt software's/modules in almost all programming languages to interact with these files. Example of JSON Data Representation:As shown in the above sample, JSON files store the data in the form of key: value pairs and sequences like lists, arrays, etc. This tutorial explains Python's way of parsing a JSON file. Package: json Python has an inbuilt package built to interact with these files called "json". the programmer must import this package into the code to work with the data from json files. So, the very first line of code a programmer has to start with is: Equivalent Data Types in Python with json Files:
In the above representation of student information as a json file, numbers, strings, and arrays are used. Working with json files in Python, there are 2 possible mechanisms:
This article discusses the parsing concept for which de-serialization is the concept.
load() and loads()1. The purpose of the load() method is to read a given JSON file. Syntax: 2. The purpose of the loads() method is to convert the data in the JSON file into a Python dictionary, thus decoding the data. Syntax: Example: Output:  Point to Remember: The JSON object we provide to loads() can be a string, bytes, or a byte array but not a dictionary. In the above code, a multi-line string is given using """.
Difference between load() and loads():Both load() and loads() de-serializes JSON data into a Python dictionary. The difference is that the load() method takes a file as input, reads it, and converts it to a Python dictionary. In contrast, the loads() method takes JSON data as input in the form of native JSON string/bytes or byte array and converts it into a Python dictionary. To Read a JSON File in Python:Suppose some JSON data is stored in a file, say "samplefile.json". To parse the file's data, we need to read the file using the load() method. 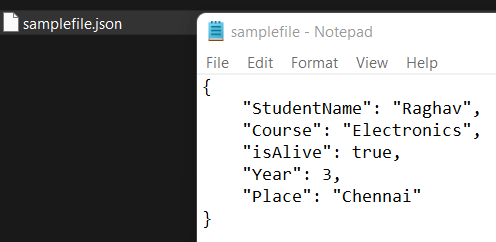 Code: Output:  Extended Syntax of load() and loads():load():
loads():s: The JSON data to be parsed
object_hook and object_pairs_hook Parameters: Output: 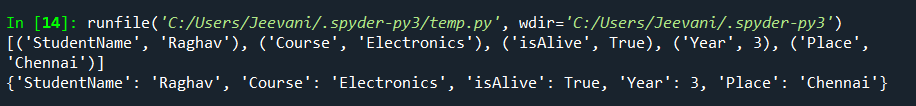 Understanding: The JSON data is parsed as a dictionary when the object_pairs_hook parameter is printed and parsed as a list of tuples when the object_hook parameter is printed. |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










