How to Iterate through a List in PythonLists are one of the most used data structures in Python. We keep using lists in many different applications, from solving simple problems to complex problems. In Python, lists replace arrays with advantages like:
We can access the data simply from lists as ordered; unlike in sets, the data will be unordered. To access the data, we can use several ways to iterate through each element inside a list. This tutorial covers all the ways with examples. 1. Loops
Output: 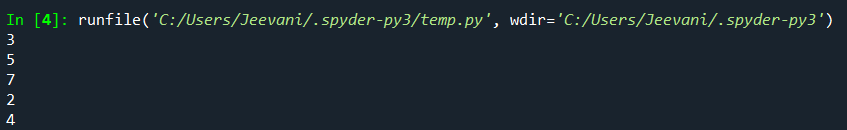 Understanding: We created a list with a few elements. Initially, count = 0. We're printing the element at the 'count' index and incrementing the count in the while loop. When the count reaches the length of the list, the loop will be terminated, and all the elements will already be accessed. Mechanism:
Output: 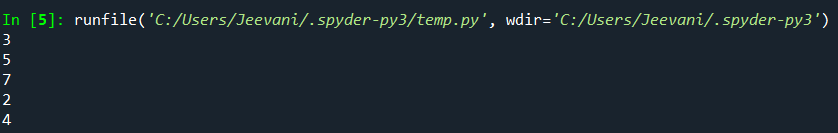 Understanding: Using for-in, we accessed all the i's, the elements inside the list.
Output: 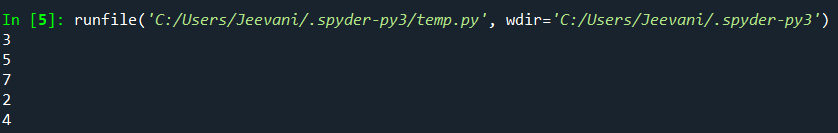 Understanding: The range function helps the 'for' loop to iterate from 0 to the given list's length. Mechanism:
2. Using List ComprehensionThis is the simple and suggested way to iterate through a list in Python. Code: Output: 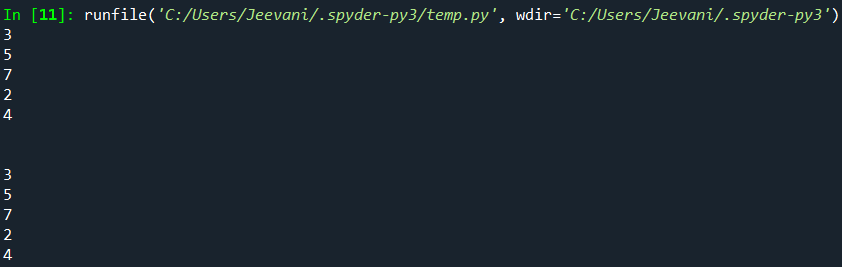 Understanding: We can use for loops inside a list comprehension. We used the same for loops we used in the above examples but inside a list in a single line. This way, we can reduce the length of the code and also list comprehension is a very subtle and efficient way to put loops in lists. 3. Using enumerate():The enumerate function converts the given list into a list of tuples. Another important fact about this function is that it keeps count of the iterations. This is a built-in function in Python. Code: Output: 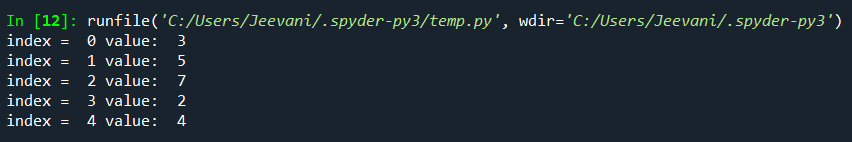 4. Using lambda function and map():These are anonymous functions. There is a function map () in Python that can accept a function as an argument, and it calls the function with every element in the iterable, and a new list with all the elements from the iterable will be returned. Code: Output:  Understanding: The lambda num: num is given as an input to the map function along with the list. The function will take every single element in the list, accept it, and then return it. The map () function will pass the list elements one by one to the lambda function to return the elements. What if we want to Iterate Multi-dimensional Lists?There is an inbuilt module in Python designed to perform operations on multi-dimensional lists. 1. To get numpy: Check if Python and pip are installed by opening the cmd via search and typing the commands: Python -version Pip --version If both Python and PIP are present in our system, it is now time to install our library: 2. Open cmd from the start menu 3. Type the command pip install numpy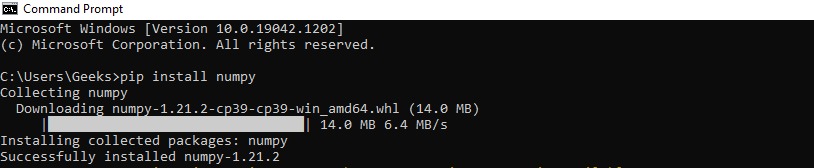 All the library packages, data, and sub-packages will be installed one after the other. Code: Output: 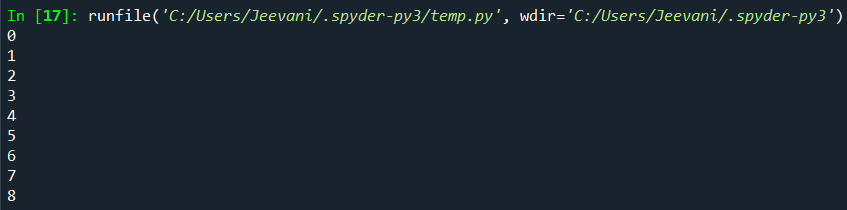 Understanding: We imported the numpy module. Using the arrange method, we created an array with 9 elements. We accessed the list by reshaping it to 3 * 3 (rows * columns) using the reshape. Using the nditer function, we printed each element in the list. Next TopicHow to Learn Python Online |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










