How to handle cookies in Django - The way to set cookiesHandling cookies are the importance concept of the web application. Django provides a straightforward way to interact with cookies. Cookies allow us to store and retrieving the data that is saved in the session. Session and Cookies are different from each other, which we will discuss in the further tutorial. These cookies are defined with the time limit; these will automatically delete after a specified time. When we visit any website and log in to that page, it asks for the storage of our user id and password and the auto-filling of a few details based on our previous logged-in session. These all process is accomplished by the cookies. In Addition, we can store the cookie on the client computer to make user interaction easier. This tutorial will discuss how we can manage the cookie in Django and why they are useful on the internet. We will also discuss how to create cookies using the server. Let's have an introduction to the cookies. What are the cookies in Django?Cookies are also known as HTTP cookies. It is a small text file created by the web browser and maintains in response to a specific Web-Server request. The text file saves locally on the computer, and most browsers will show the cookies generated under the Privacy and Security settings. The request is sent by the user using the HTTP protocol, but this is stateless. It won't help to recognize whether the user is new or has previously visited the site. The cookie contains the unique session id used to identify the user and other relevant information to the website context. The website sends the cookie with the unique user identity when we log in to a website. Cookies provide many facilities that are not possible with HTTP. How to Django Cookies Work?Let's understand how the cookie works on the internet.
Cookies are used for various purposes, such as login to a website or online shopping. Many companies use as to track user preference. Cookies are used differently by various websites depending on their needs. Why we need cookies in Django?When we log in to an eCommerce site or Facebook without signing out, it remains signed for the next time we visit our account. Cookies are used to accomplish this (which contains user-session information). Cookies are also used for product recommendations on several eCommerce websites. Cookies Attributes in DjangoA cookie attribute can perform two tasks - it can set cookies to the user computer and access those cookies. Let's understand these concepts in detail. Set cookies in DjangoThis attributes is used to set cookies that the server sends to the user's browser to save the data. Below is the syntax of cookie() method. name - It specifies the cookie name. value - It is used to the specifies the specific value that we want to store in the user computer. max_age - It is used to define the time limit of the cookie. If time limit is not specified, it will active until the browser is closed. Expires - It is a string in the format "Wdy DD-Mon-YY HH:MM:SS GMT or a datetime. The max_age will be determined if expires is a datetime object. Get cookies in DjangoThe server uses the get cookies to read the previously delivered cookies data. We can use the following syntax. Let's see how we can set the Django cookies manually. Django Cookie ImplementationIn the following steps, we will set the cookie using Django. Create the all required configuration and include the following code in view.py. Now, map this view to urls.py.  Here, we will write the view for the get cookies. view.py urls.py Output:  Explanation of the above code - In the above view.py, we have used the HttpResponse method that displays any output to the screen. We define the cookie in the separate functions - The first function will set the cookies to the user's computer and second function with the variable in the COOKIE appended to it for displaying or receiving the cookie that has been set. Now, run the server using the following command. Updating CookieWe can modify a defined cookie. Let's see the following example. After the updating the cookie, we need to append it into the urls.py file. Now, we run the server and visit the below page. Output:  Instead of using Httpresponse we can use the redirect function to update a cookie. Yet, here we will use the set cookies function. Now, we will add the update using the render function. Delete Cookie in DjangoNow, we will learn how to delete the cookies already placed in the user's computer. As we know that there is an optional parameter max_age that deleted the cookie session by default. To delete the cookie, we add the following code in views.py file. Now, we add this view to urls.py file. Output:  Difference Approach to Handle CookieThe 'expires' attribute can be used for handling the end of cookie session. We can modify the expire function and know how to delete a cookie. Let's see the following syntax. Read Cookie from RequestCookies are sent with the user request by the website. As a result, the server obtains a cookie with each request. Django provides the easy way to access the cookie.
We have discussed in above section.
Using this method on the request object, we can easily get the particular value. Below is the syntax of this method. 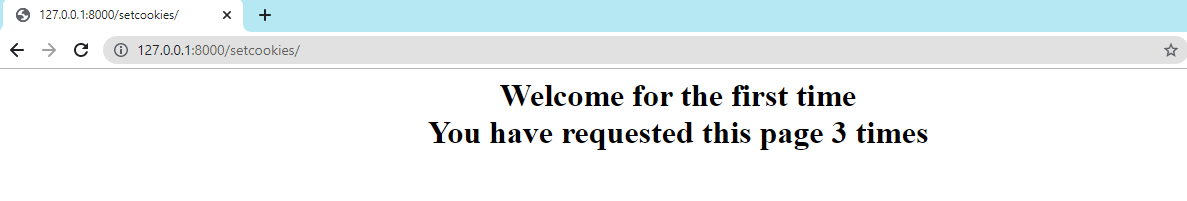 We will need to redirect(), so import it now. We will need to redirect(), so import it now. Code for cookies Output 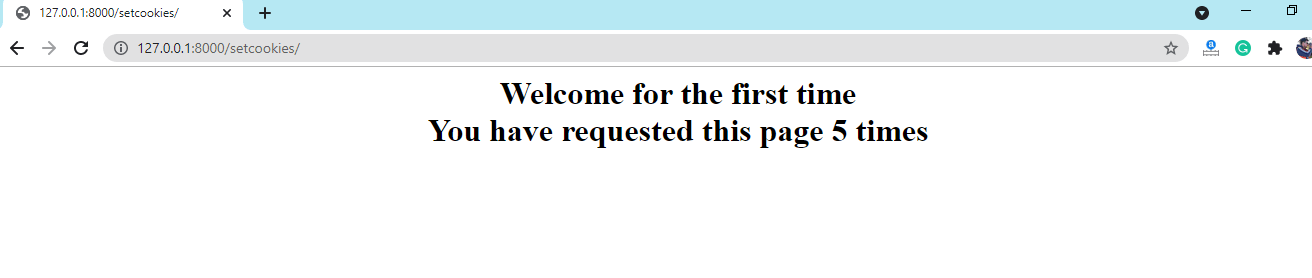 Django Cookie Enable and DisableThe settings Python file defines which cookies are enabled and disabled. The session variable is available in the settings that are used to handle session cookies. We can enable and disable the cookie manually by setting, updating, and deleting cookies. There are session-level cookies that can be set to true if necessary. By default, they are set to FALSE. Cookies are encrypted, so these are quite secure. The session cookie can be used to track how many times a user visits a specific website. Important Points of CookiesBelow are some important points that you should keep in mind.
An Issue with Django Cookie SecurityAlong with the advantages of cookies, there are disadvantages of the cookies.
Limitation of the Django Cookies
ConclusionWe have discussed all the important concept of the Django cookies and how we can use them into our projects. We have defined how to set, get, update and delete the cookies. The cookies help to identify the user and quick retrieval of data. The system doesn't always go to the database, and search for it, return the result to the user. Next Topicagg() function in Python |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










