Getopt module in PythonThe getopt modules is analyser used for command-line options, which are based on the convention organized by the UNIX getopt() function. It is basically used to analysing an argument sequence like sys.argv. We can also understand this module as it helps the scripts to analyse the command - line arguments in sys.argv. This module works like the C programming language getotp() function for analysing the command - line parameters. Python getopt FunctionThis modules provide some primary function that is the (goes by the same name that is) getopt(). The functionality of this function is to analyse command - line options and parameter lists. Syntax: Parameters: The getopt.getopt() module takes the following parameters. args: The args is the list of arguments which are to be passed options: The options are the string of options letters which the script wants to recognize. The option that needs arguments should be written with a colon ( :). long_options: This is the list of the string which have the name of long options. The option that needs arguments should be written with an equal sign ( = ). Return Type: The return value of getopt () module function consists of two elements. The first element of the return value is the list of ( option , value ) pairs, and the second element of the return value is a list of program arguments which are left when the options list was stripped. Supported option syntax includes: Function Arguments of Getopt()The getopt ( ) module function takes three arguments:
Users can combine the Long and short form of the options in a single call. Short Form Options:Suppose the user's program is taking two options ' - a ' and ' - b ' with the ' - b ' option needs an argument, then the value must be " ab: ". Long-form options in Getopt ( )If the user's program wants to take two options, such as, " - noarguement " and " - witharguement " then, the sequence of the arguements will be [ ' noarguement ' , ' witharguement= ' ]. Example 1:Output: 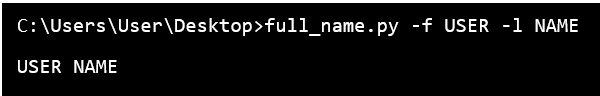 Here, the user has created a function full_name(), which will print the full name of the user after receiving the first name and last name from the command line. The user has also abbreviated the first name as ' f ' and the last name as ' l '. Example 2:In this example, the user can use the full form as ' first_name ' and ' last_name ' instead of using the short form as ' f ' and ' l '. Output: 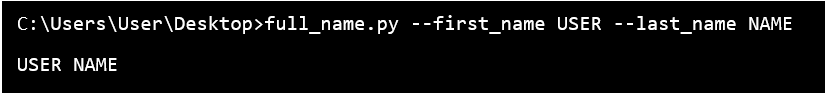 The user has to remember that the single dash ( ' - ' ) for short forms of the arguments and for long forms of the arguments users should use the double dash ( ' -- ' ). Conclusion:In this article, we have discussed the getopt() module and its functions and their arguments. We have also explained the different implementing forms with proper rules in the command line prompt, with well-defined examples. Next TopicMerge two Dictionaries in Python |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










