Functions and file objects in Python sys modulesys stands for the system. The module consists of various functions and variables that help the programmer to manipulate Python's run-time and compile-time environment settings. It directly interacts with and operates the Python Interpreter. The first step in using the functionality of the sys module is to import the module into the program using the statement: In this tutorial, we'll cover these contents:
Basic functions and variables in the sys module:
Now that we covered the basic built-in functions and attributes in the sys module, we'll learn about the standard streams: First, what is a stream? To execute a program:
The data source, program, and destination interactions are called streams. Python interacts with the input, output devices via the standard input, and output stream objects in the sys module called stdin and stdout: stdinstdin-standard input. It is a predefined input stream object that handles the data flow into the program from sources. For example, the user gives input via the keyboard. When we write input(), the function reads the bytes from a standard input stream device, usually a keyboard. The built-in function input() abstracts all of the mechanisms. It is the wrapper function of sys.stdin.readline(). We can even redirect the input source from the keyboard to another device or a file. Here is a simple example for taking input using stdin: 1. Open notepad or another text editor. 2. Enter the code snippet and save it as a python file(.py) You can observe that in the above snippet, sys.stdin acts like a file, and using readlines(), we are reading it. 3. Now, open command prompt: Change the directory to the file location using the command: 4. Enter the input and kill it using Ctrl+ z. You will be able to see all the inputs entered along with the length. 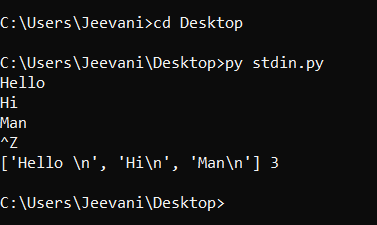 5. We took input from the user directly from the command line. sys.stdin.readline() and input():We can use both functions to take input in Python. There are some notable differences between their functionalities:
stdout:stdout: standard output. It is a predefined output stream object that handles the data from the program to different destinations. For example, we use print() to display something on the console/ screen. Here, the standard output stream device is the console. It allows us to interact directly with the command line and print something to it. Here is a simple example: 1. Open notepad or another text editor. 2. Enter the code snippet and save it as a python file(.py) You can observe that in the above snippet, sys.stdout acts like a file, and using write(), we are writing to it. 3. Now, open command prompt: Change the directory to the file location using the command: 4. Enter the input and kill it using Ctrl+ z. You will be able to see all the inputs entered along with the length. 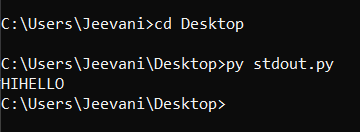 5. As you can observe, the function sys.stdout.write() doesn't, by default, add a new line escape character at the end. We need to add it. stderr:stderr: Standard error stream. Like the stdout stream, stderr also is an output stream. The difference between stdout and stderr is that stderr is used to print or output errors, exceptions, and debug information conventionally. The standard error stream device is the console. We can also use stdout to output error information, but stderr is specially designed for this task. Here is a simple example: 1. Open notepad or another text editor. 2. Enter the code snippet and save it as a python file(.py) You can observe that in the above snippet, sys.stderr acts like a file, and using write(), we are writing to it. 3. Now, open command prompt: Change the directory to the file location using the command: 4. Enter the input and kill it using Ctrl+ z. You will be able to see all the inputs entered along with the length. 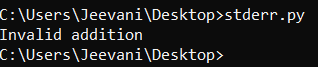 5. This function also writes to the IDE console, unlike stdout.write():  Redirection:Generally, the standard input stream device is a keyboard, and the standard output stream device is the system console. We can change these devices according to our needs by 1. Shell redirection.
Here is an example:
3. Now, open command prompt: Change the directory to the file location using the command: Use the command: to redirect the output of source.py to the destination file. 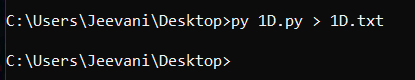 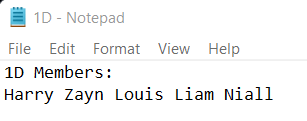 2. sing stdout: 1D.txt: 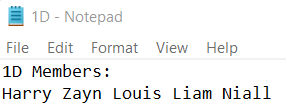 Next TopicWhat is a Binary Heap in Python |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










