FastNlMeansDenoising in PythonIn this article, we will learn about noise, various types of noises, Image denoising, Image Denoising with OpenCV, nonlocal means algorithms in OpenCV, and fastNlMeansDenosiong functions in OpenCV. fastNIMeansDenoising is a method of OpenCV module. This is used to denoise the image. The process of taking out undesirable noise from an image before analysis is called denoising. It refers to a significant preprocessing phase. Denoising is one of the most important phases of preprocessing the image. It is used to remove the noise from the image so let's first understand what the noise is. Noise in ImageThe presence of defects in an image is known as noise that is unrelated to the underlying scene content. Statistical variations of a measurement produced by a random process are, in general, considered to be noise. In imaging, noise manifests as an artifact that covers the image in a grainy texture. In an image, noise can take on a variety of shapes and manifestations and is typically an unwelcome or distressing artifact that degrades the subjective visual quality. The image has two main types of noise 1. Salt and paper noise: It features sporadic dark and light disruptions. The distinguishing feature is that the value of a noisy pixel has no bearing on the color of other pixels. The pixels in the image are significantly different from one another in color or intensity from their surrounding pixels. In most cases, this kind of noise will only have a little impact on a few image pixels. The name "salt and pepper noise" refers to the appearance of the image, which contains white and dark dots. 2. Gaussian noise: A (typically) modest amount will be added or subtracted from each pixel's original value in the image. A histogram, which displays a normal distribution of noise, plots the degree of distortion of a pixel value against its frequency. Although other distributions are feasible, the central limit theorem, which states that the total of several noises tends to approach a Gaussian distribution, makes the Gaussian (normal) distribution a generally reliable model. Now we have to understand, what noise in images is. Now it's time to understand what is denoising. Image DenoisingImage denoising is one of the fundamental problems in computer vision and image processing. Denoising estimates the original image by reducing the amount of noise in the image. Image noise can come from a variety of sources (such as the environment or the sensor), and in real-world applications, it's frequently impossible to prevent them. In light of this, picture denoising is crucial in a variety of applications, including image restoration, visual tracking, image registration, and image segmentation. Even though a variety of algorithms have been put out for the goal of image denoising, the issue of image noise suppression continues to be a difficult one, particularly when the photographs are taken in unfavorable conditions and have a high degree of noise. Now we have seen what is the image denoising. Now we will understand the various method of openCV to denoising the image. Image Denoising by Using OpenCVThe OpenCV module has various nonlocal means algorithms to denoise the image. Before seeing the various method in OpenCV let's understand the mean of nonlocal mean algorithms Nonlocal means algorithmThe fundamental principle of the nonlocal means algorithm is to average the colors of many image sub-windows that are similar to the one that makes up the pixel neighborhood to replace the color of a pixel. We now know what the nonlocal means algorithm's mean is. Now let's look at the various functions in the OpenCV module to denoise the image. There are four versions of this algorithm are available in OpenCV.
fastNlMeansDenoising() Function in PythonIt is a nonlocal means algorithm base function. This function is used with single gray-scale images to denoise the image. Syntax of the fastNlMeansDenoising() function Parameter of the fastNlMeansDenoising() function
Note: The function transforms the image to CIELAB colorspace and uses the fastNlMeansDenoising function to independently denoise the L and AB components with the supplied h parameters.Let's understand how we can remove the noise from the image with the help of an example Removing the salt and paper noise from the imageRandom bright pixels and random dark pixels are added to an image to add salt and pepper noise. Because it statistically reduces the original data values, this model is often referred to as data drop noise. Source: A camera's sensor cell that is malfunctioning.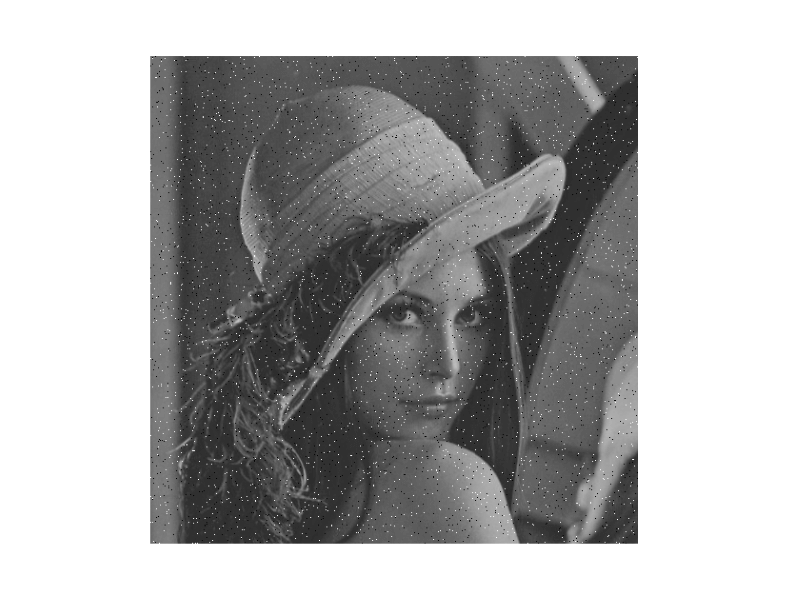  In the above image, we have seen the salt and paper noise. The image has some bright pixels in the dark area. So let's see the python code to reduce or remove the salt and paper noise with the help of the openCV module. Output: 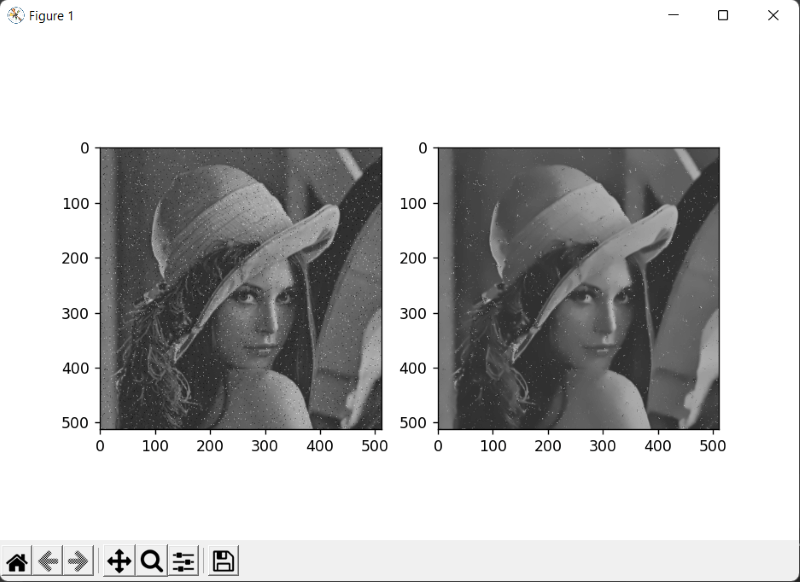 In the above example, we first imported all the required libraries in the code. This is a salt and paper noise image. Now we will use cv2.imread() image to read the image. The image should be a black and white 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel, or 4-channel image. Now we will use the cv2.fastMlMeansDenoising() to denoise the salt and paper noise. Now we will use the pyplot to visualize the image. Removing the gaussian noise from the imageThe most prevalent kind of noise in digital images is gaussian. Due to sensor constraints during picture collection in low-light situations, which make it challenging for the visible light sensors to adequately record scene details, Gaussian noise occurs in digital imaging.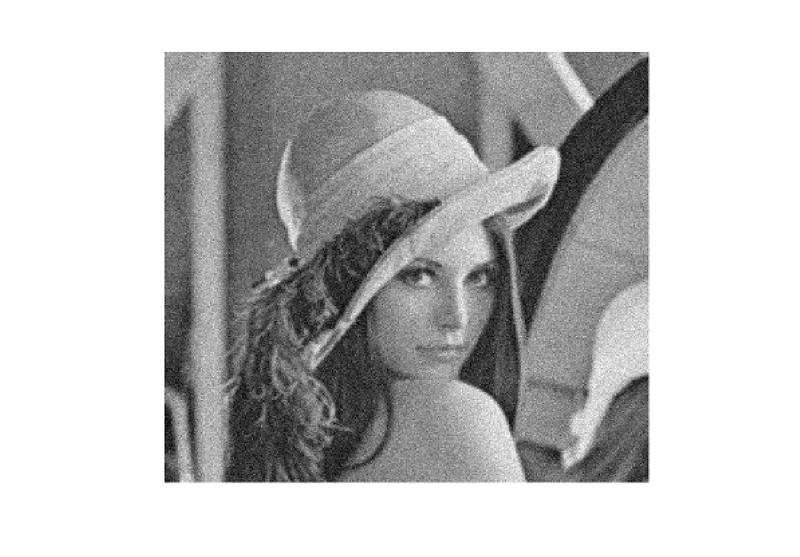  In the above example, we have seen that the image is noisy. This image is an example of Gaussian noise. Let's see the python code to remove the gaussian noise with the help of the openCV module. Output 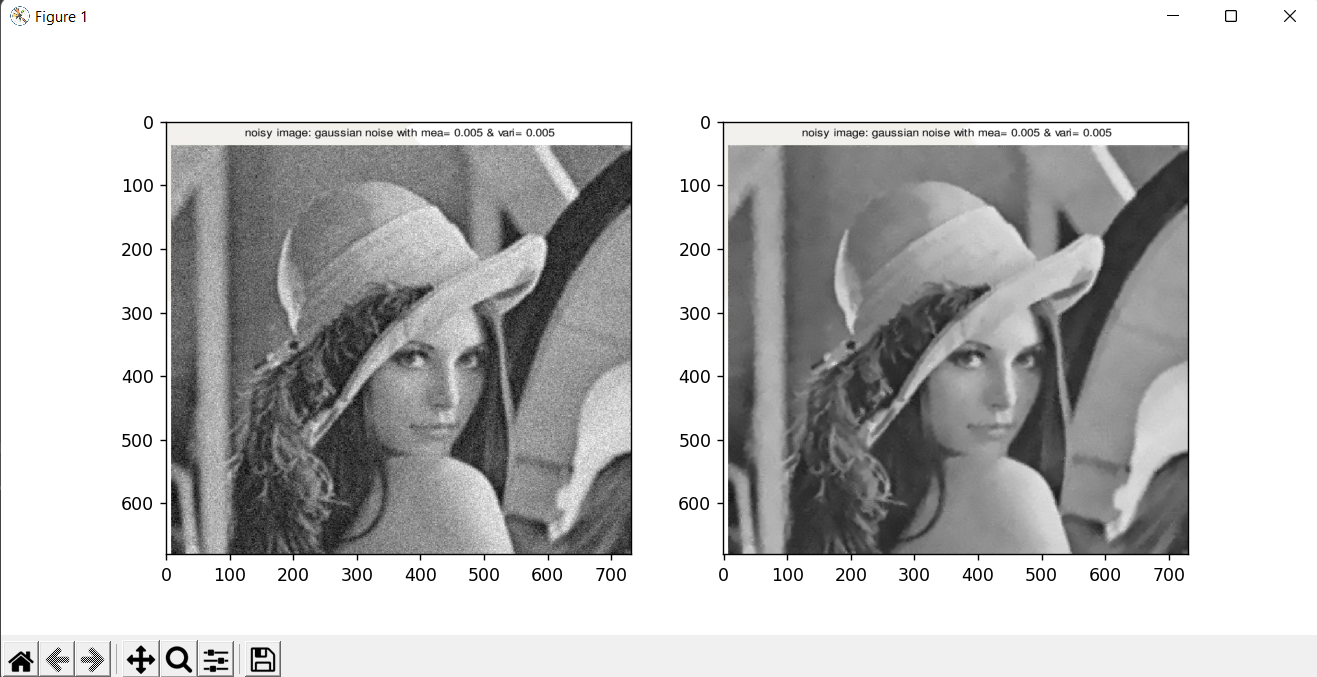 In the above example, we first imported all the required libraries in the code. This is a gaussian noise image. Now we will use cv2.imread() image to read the image. The image should be a black and white 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel, or 4-channel image. Now we will use the cv2.fastMlMeansDenoising() to denoise the salt and paper noise. Now we will use the pyplot to visualize the image. ConclusionIn this article, we have discussed noise various types of noises. Then we have discussed what Image denoising and its features it is and, Image Denoising with OpenCV and nonlocal means algorithms in OpenCV, and fastNlMeansDenosiong functions in OpenCV. Next TopicPython Email.utils |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










