Django ViewsA view is a place where we put our business logic of the application. The view is a python function which is used to perform some business logic and return a response to the user. This response can be the HTML contents of a Web page, or a redirect, or a 404 error. All the view function are created inside the views.py file of the Django app. Django View Simple Example//views.py Let's step through the code. First, we will import DateTime library that provides a method to get current date and time and HttpResponse class. Next, we define a view function index that takes HTTP request and respond back. View calls when gets mapped with URL in urls.py. For example Output: 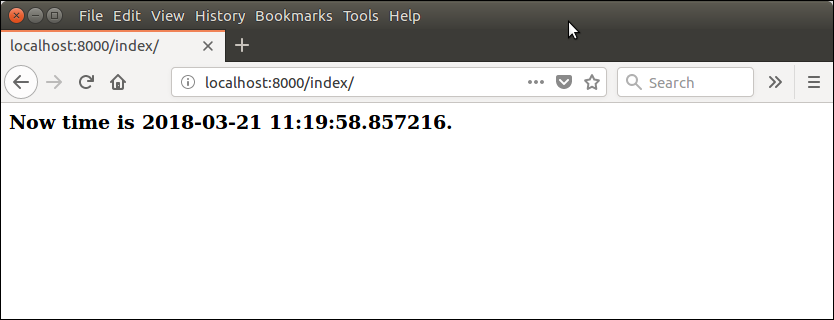 Returning ErrorsDjango provides various built-in error classes that are the subclass of HttpResponse and use to show error message as HTTP response. Some classes are listed below.
Django View Example// views.py Output: 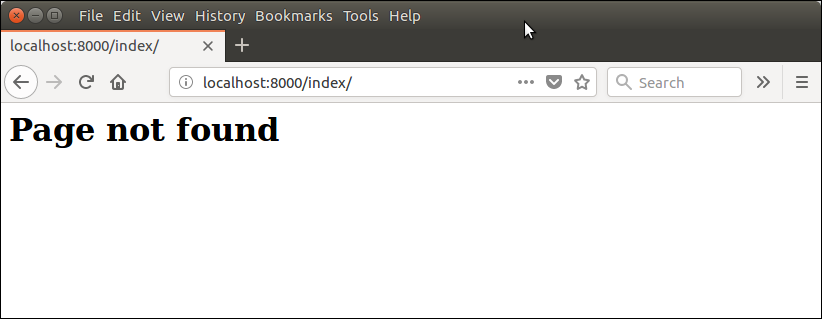 Django View HTTP DecoratorsHTTP Decorators are used to restrict access to view based on the request method. These decorators are listed in django.views.decorators.http and return a django.http.HttpResponseNotAllowed if the conditions are not met. Syntax require_http_methods(request_method_list) Django Http Decorator Example//views.py This method will execute only if the request is an HTTP GET request. //urls.py Output: 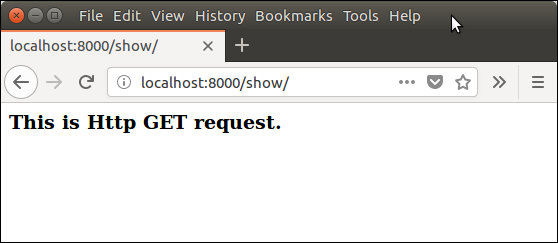 Next TopicTemplate |