Deletion in Red-Black Tree using PythonRed-Black TreesA red-black tree is a binary search tree with the additional property of being "nearly" adjusted. Every node in a red-black tree has a color, either red or black, and these colors are utilized to keep up with balance during insertions and deletions. Deletion:BST Deletion: Begin by finding the node you need to erase utilizing standard BST deletion. Assuming the node has one or no children, eliminate it and supplant it with its child (if any). Save the shade of the node to be erased, as it will be required later to decide if to apply the "erase fix." Fix Violations (Erase Fix): Like insertion, deletion could disregard red-black tree properties, especially the double-black property. You want to play out a progression of recoloring, rotation, and substitution tasks known as the "erase fix."
Code Output: The initial starting tree: 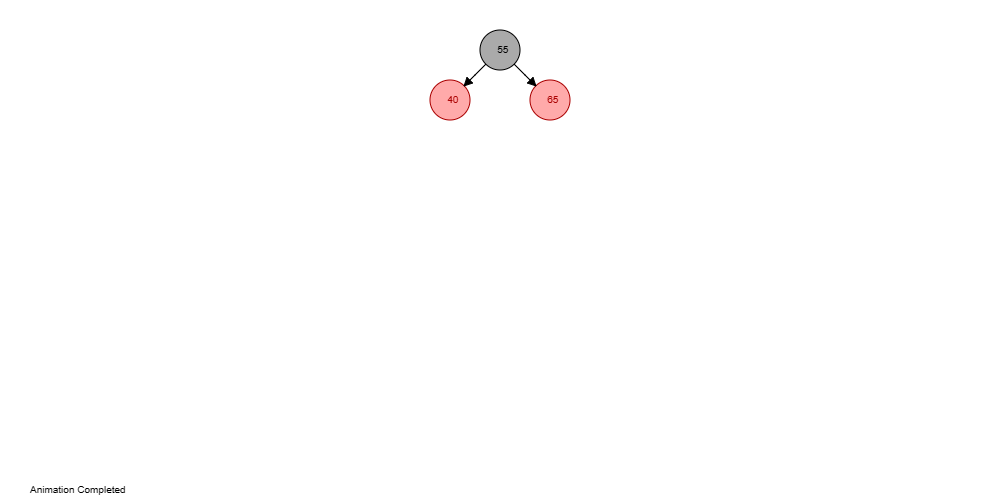 After deleting element 40: 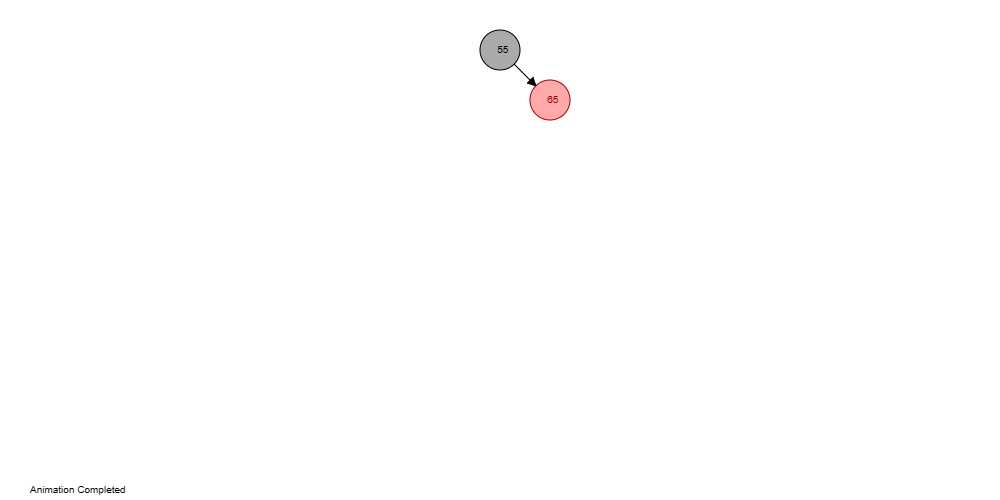 After deleting element 65:  Executing these means accurately guarantees that insertion and deletion activities perform well and keep up with the helpful properties of the tree. |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India










