 C++ Interview QuestionsA list of top frequently asked C++ interview questions and answers are given below. 1) What is C++?C++ is an object-oriented programming language created by Bjarne Stroustrup. It was released in 1985. C++ is a superset of C with the major addition of classes in C language. Initially, Stroustrup called the new language "C with classes". However, after sometime the name was changed to C++. The idea of C++ comes from the C increment operator ++. 2) What are the advantages of C++?C++ doesn't only maintains all aspects from C language, it also simplifies memory management and adds several features like:
3) What is the difference between C and C++?Following are the differences between C and C++:
4) What is the difference between reference and pointer?Following are the differences between reference and pointer:
5) What is a class?The class is a user-defined data type. The class is declared with the keyword class. The class contains the data members, and member functions whose access is defined by the three modifiers are private, public and protected. The class defines the type definition of the category of things. It defines a datatype, but it does not define the data it just specifies the structure of data. You can create N number of objects from a class. 6) What are the various OOPs concepts in C++?The various OOPS concepts in C++ are: 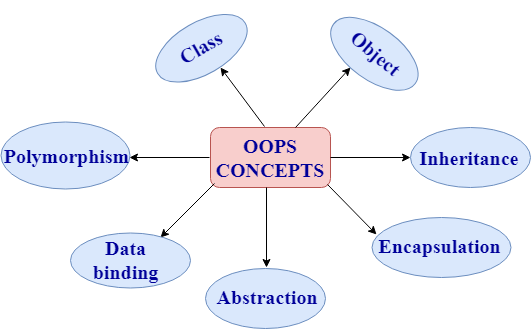
The class is a user-defined data type which defines its properties and its functions. For example, Human being is a class. The body parts of a human being are its properties, and the actions performed by the body parts are known as functions. The class does not occupy any memory space. Therefore, we can say that the class is the only logical representation of the data. The syntax of declaring the class:
An object is a run-time entity. An object is the instance of the class. An object can represent a person, place or any other item. An object can operate on both data members and member functions. The class does not occupy any memory space. When an object is created using a new keyword, then space is allocated for the variable in a heap, and the starting address is stored in the stack memory. When an object is created without a new keyword, then space is not allocated in the heap memory, and the object contains the null value in the stack. The syntax for declaring the object:
Inheritance provides reusability. Reusability means that one can use the functionalities of the existing class. It eliminates the redundancy of code. Inheritance is a technique of deriving a new class from the old class. The old class is known as the base class, and the new class is known as derived class. Syntax Note: The visibility-mode can be public, private, protected.
Encapsulation is a technique of wrapping the data members and member functions in a single unit. It binds the data within a class, and no outside method can access the data. If the data member is private, then the member function can only access the data.
Abstraction is a technique of showing only essential details without representing the implementation details. If the members are defined with a public keyword, then the members are accessible outside also. If the members are defined with a private keyword, then the members are not accessible by the outside methods.
Data binding is a process of binding the application UI and business logic. Any change made in the business logic will reflect directly to the application UI.
Polymorphism means multiple forms. Polymorphism means having more than one function with the same name but with different functionalities. Polymorphism is of two types:
7) What are the different types of polymorphism in C++?Polymorphism: Polymorphism means multiple forms. It means having more than one function with the same function name but with different functionalities. Polymorphism is of two types: 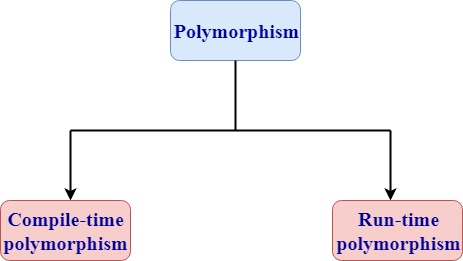
Runtime polymorphism is also known as dynamic polymorphism. Function overriding is an example of runtime polymorphism. Function overriding means when the child class contains the method which is already present in the parent class. Hence, the child class overrides the method of the parent class. In case of function overriding, parent and child class both contains the same function with the different definition. The call to the function is determined at runtime is known as runtime polymorphism. Let's understand this through an example: Output: javaTpoint tutorial
Compile-time polymorphism is also known as static polymorphism. The polymorphism which is implemented at the compile time is known as compile-time polymorphism. Method overloading is an example of compile-time polymorphism. Method overloading: Method overloading is a technique which allows you to have more than one function with the same function name but with different functionality. Method overloading can be possible on the following basis:
Let's understand this through an example: Output: 6 24
8) Define namespace in C++.
Syntax of accessing the namespace variable: Let's understand this through an example: Output: 10 9) Define token in C++.A token in C++ can be a keyword, identifier, literal, constant and symbol. 10) Who was the creator of C++?Bjarne Stroustrup. 11) Which operations are permitted on pointers?Following are the operations that can be performed on pointers:
There are two types of increment pointers: 1. Pre-increment pointer: The pre-increment operator increments the operand by 1, and the value of the expression becomes the resulting value of the incremented. Suppose ptr is a pointer then pre-increment pointer is represented as ++ptr. Let's understand this through an example: Output: Value of *ptr is : 1 Value of *++ptr : 2 2. Post-increment pointer: The post-increment operator increments the operand by 1, but the value of the expression will be the value of the operand prior to the incremented value of the operand. Suppose ptr is a pointer then post-increment pointer is represented as ptr++. Let's understand this through an example: Output: Value of *ptr is : 1 Value of *ptr++ : 1
12) Define 'std'.Std is the default namespace standard used in C++. 13) Which programming language's unsatisfactory performance led to the discovery of C++?C++was discovered in order to cope with the disadvantages of C. 14) How delete [] is different from delete?Delete is used to release a unit of memory, delete[] is used to release an array. 15) What is the full form of STL in C++?STL stands for Standard Template Library. 16) What is an object?The Object is the instance of a class. A class provides a blueprint for objects. So you can create an object from a class. The objects of a class are declared with the same sort of declaration that we declare variables of basic types. 17) What are the C++ access specifiers?The access specifiers are used to define how to functions and variables can be accessed outside the class. There are three types of access specifiers:
18) What is Object Oriented Programming (OOP)?OOP is a methodology or paradigm that provides many concepts. The basic concepts of Object Oriented Programming are given below: Classes and Objects: Classes are used to specify the structure of the data. They define the data type. You can create any number of objects from a class. Objects are the instances of classes. Encapsulation: Encapsulation is a mechanism which binds the data and associated operations together and thus hides the data from the outside world. Encapsulation is also known as data hiding. In C++, It is achieved using the access specifiers, i.e., public, private and protected. Abstraction: Abstraction is used to hide the internal implementations and show only the necessary details to the outer world. Data abstraction is implemented using interfaces and abstract classes in C++. Some people confused about Encapsulation and abstraction, but they both are different. Inheritance: Inheritance is used to inherit the property of one class into another class. It facilitates you to define one class in term of another class. 19) What is the difference between an array and a list?
20) What is the difference between new() and malloc()?
21) What are the methods of exporting a function from a DLL?There are two ways:
22) Define friend function.Friend function acts as a friend of the class. It can access the private and protected members of the class. The friend function is not a member of the class, but it must be listed in the class definition. The non-member function cannot access the private data of the class. Sometimes, it is necessary for the non-member function to access the data. The friend function is a non-member function and has the ability to access the private data of the class. To make an outside function friendly to the class, we need to declare the function as a friend of the class as shown below: Following are the characteristics of a friend function:
Let's understand this through an example: Output: 11 23) What is a virtual function?
Rules of a virtual function:
24) When should we use multiple inheritance?You can answer this question in three manners:
25) What is a destructor?A Destructor is used to delete any extra resources allocated by the object. A destructor function is called automatically once the object goes out of the scope. Rules of destructor:
26) What is an overflow error?It is a type of arithmetical error. It happens when the result of an arithmetical operation been greater than the actual space provided by the system. 27) What is overloading?
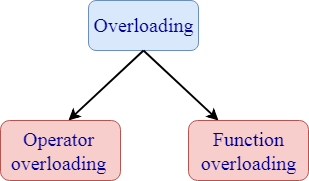 1. Operator overloading: Operator overloading is a compile-time polymorphism in which a standard operator is overloaded to provide a user-defined definition to it. For example, '+' operator is overloaded to perform the addition operation on data types such as int, float, etc. Operator overloading can be implemented in the following functions:
Syntax of Operator overloading: 2. Function overloading: Function overloading is also a type of compile-time polymorphism which can define a family of functions with the same name. The function would perform different operations based on the argument list in the function call. The function to be invoked depends on the number of arguments and the type of the arguments in the argument list. 28) What is function overriding?If you inherit a class into a derived class and provide a definition for one of the base class's function again inside the derived class, then this function is called overridden function, and this mechanism is known as function overriding. 29) What is virtual inheritance?Virtual inheritance facilitates you to create only one copy of each object even if the object appears more than one in the hierarchy. 30) What is a constructor?A Constructor is a special method that initializes an object. Its name must be same as class name. 31) What is the purpose of the "delete" operator?The "delete" operator is used to release the dynamic memory created by "new" operator. 32) Explain this pointer?This pointer holds the address of the current object. 33) What does Scope Resolution operator do?A scope resolution operator(::) is used to define the member function outside the class. 34) What is the difference between delete and delete[]?Delete [] is used to release the array of allocated memory which was allocated using new[] whereas delete is used to release one chunk of memory which was allocated using new. 35) What is a pure virtual function?The pure virtual function is a virtual function which does not contain any definition. The normal function is preceded with a keyword virtual. The pure virtual function ends with 0. Syntax of a pure virtual function: Let's understand this through an example: Output: javaTpoint 36) What is the difference between struct and class?
37) What is a class template?A class template is used to create a family of classes and functions. For example, we can create a template of an array class which will enable us to create an array of various types such as int, float, char, etc. Similarly, we can create a template for a function, suppose we have a function add(), then we can create multiple versions of add(). The syntax of a class template: Syntax of a object of a template class: 38) What is the difference between function overloading and operator overloading?Function overloading: Function overloading is defined as we can have more than one version of the same function. The versions of a function will have different signature means that they have a different set of parameters. Operator overloading: Operator overloading is defined as the standard operator can be redefined so that it has a different meaning when applied to the instances of a class. 39) What is a virtual destructor?A virtual destructor in C++ is used in the base class so that the derived class object can also be destroyed. A virtual destructor is declared by using the ~ tilde operator and then virtual keyword before the constructor. Note: Constructor cannot be virtual, but destructor can be virtual.Let's understand this through an example
Output: Base constructor is called Derived class constructor is called Base class object is destroyed In the above example, delete b will only call the base class destructor due to which derived class destructor remains undestroyed. This leads to the memory leak.
Output: Base constructor is called Derived class constructor is called Derived class object is destroyed Base class object is destroyed When we use the virtual destructor, then the derived class destructor is called first, and then the base class destructor is called. |