Artificial Intelligence Multiple Choice Questions1) Artificial Intelligence is about_____.
Answer: b. Making a machine Intelligent. Explanation: Artificial Intelligence is a branch of Computer science, which aims to create intelligent machines so that machine can think intelligently in the same manner as a human does. 2) Who is known as the -Father of AI"?
Answer: c. John McCarthy Explanation: John McCarthy was a pioneer in the AI field and known as the father of Artificial intelligence. He was not only the known as the father of AI but also invented the term Artificial Intelligence. 3) Select the most appropriate situation for that a blind search can be used.
Answer: b. Small Search Space Explanation: Blind Search is also known as uninformed search, and it does not contain any domain information such as closeness, location of the goal, etc. Hence the most appropriate situation that can be used for the blind search is Small-search Space. 4) The application/applications of Artificial Intelligence is/are
Answer: d. All of the above Explanation: All the given options are the applications of AI. 5) Among the given options, which search algorithm requires less memory?
Answer: b. Depth First Search Explanation: The Depth Search Algorithm or DFS requires very little memory as it only stores the stack of nodes from the root node to the current node. 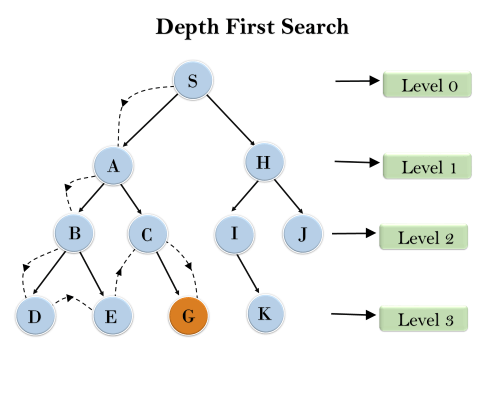 6) If a robot is able to change its own trajectory as per the external conditions, then the robot is considered as the__
Answer: d. Intelligent Explanation: If a robot is able to change its own trajectory as per the external conditions, then the robot is considered intelligent. Such type of agents come under the category of AI agents or Rational Agents. 7) Which of the given language is not commonly used for AI?
Answer: d. Perl Explanation: Among the given languages, Perl is not commonly used for AI. LISP and PROLOG are the two languages that have been broadly used for AI innovation, and the most preferred language is Python for AI and Machine learning. 8) A technique that was developed to determine whether a machine could or could not demonstrate the artificial intelligence known as the___
Answer: b. Turing Test Explanation: In the year 1950, mathematician and computing pioneer Alan Turing introduced a test to determine whether a machine can think like a human or not, which means it can demonstrate intelligence, known as the Turing Test. It was based on the "Imitation game" with some modifications. This technique is still a measure of various successful AI projects, with some updates. 9) The component of an Expert system is_________.
Answer: d. All of the above Explanation: Expert system is a part of AI and a computer program that is used to solve complex problems, and to give the decision-making ability like human. It does this with the help of a Knowledge base, Inference engine, and User interface, and all these are the components of an Expert System. 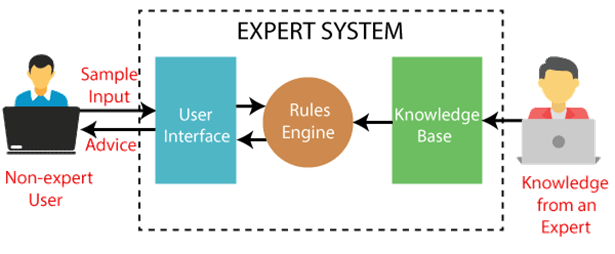 10) Which algorithm is used in the Game tree to make decisions of Win/Lose?
Answer: d. Min/Max Algorithm Explanation: A game tree is a directed graph whose nodes represent the positions in Game and edges represent the moves. To make any decision, the game tree uses the Min/Max algorithm. The Min/Max algorithm is the preferred one over other search algorithms, as it provides the best move to the player, assuming that the opponent is also playing Optimally. 11) The available ways to solve a problem of state-space-search.
Answer: b. 2 Explanation: There are only two ways to solve the problems of state-space search. 12) Among the given options, which is not the required property of Knowledge representation?
Answer: C. Representational Verification Explanation: Knowledge representation is the part of Artificial Intelligence that deals with AI agent thinking and how their thinking affects the intelligent behavior of agents. A good knowledge representation requires the following properties:
13) An AI agent perceives and acts upon the environment using___.
Answer: d. Both a and c. Explanation: An AI agent perceives and acts upon the environment using Sensors and Actuators. With Sensors, it senses the surrounding, and with Actuators, it acts on it. 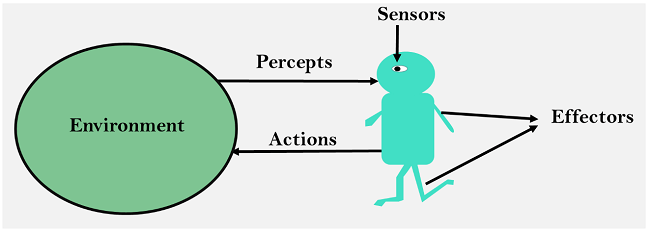 14) Which rule is applied for the Simple reflex agent?
Answer: c. Condition-action rule Explanation: The simple reflex agent takes decisions only on the current condition and acts accordingly; it ignores the rest of history; hence it follows the Condition-action rule. 15) Which agent deals with the happy and unhappy state?
Answer: a. Utility-based agent Explanation: Utility-based agent uses an extra component of utility that provides a measure of success at a given state. It decides that how efficient that state to achieve the goal, which specifies the happiness of the agent. 16) Rational agent always does the right things.
Answer: a. True Explanation: Rational agent has clear preference, goal, and acts in a way to maximize its performance. It is said that it always does the right things, which means it gives the best performance for each action. 17) Which term describes the common-sense of the judgmental part of problem-solving?
Answer: d. Heuristic Explanation: In problem-solving, the Heuristic describes the common sense or Judgemental part. 18) Which AI technique enables the computers to understand the associations and relationships between objects and events?
Answer: d. Pattern Matching Explanation: Pattern matching is a way to check a given sequence of tokens in order to determine the presence of a given character or data in the given sequence. It allows computers to understand the relationship between objects and events. 19) The exploration problem is where______.
Answer: b. Agent does not contain knowledge State and actions Explanation: In Exploration problems, the agent does not contain the knowledge of state space and actions in advance. These are difficult problems and used in the real world. 20) In the Wumpus World Problem, the reason for the uncertainty is that the agent's sensor gives only__
Answer: d. Partial & local Information Explanation: The Wumpus world is an example environment that is made of grids of squares surrounded by walls. Each square can have agents or objects. The world is used to demonstrate the worth of a knowledge-based agent and knowledge representation. In the environment, uncertainty arises as the agent can only perceive the close environment. The Wumpus world is represented in below image: 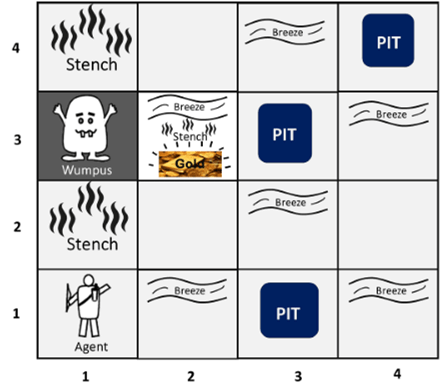 21) The search algorithm which is similar to the minimax search, but removes the branches that don't affect the final output is known as__.
Answer: c. Alpha-beta pruning Explanation: Alpha-beta pruning algorithm is the modified version of the Minimax algorithm and returns the same moves as the original algorithm, but it removes all those nodes/branches that do not affect the final decision. 22) The maximum depth to which the alpha-beta pruning can be applied.
Answer: d. Any depth Explanation: The Alpha-beta pruning can be applied to any depth of the tree and it can eliminate the entire subtree, if it is not affecting the final decision. 23) Among the given options, which is also known as inference rule?
Answer: c. Resolution Explanation: Resolution is also known as inference rule as it shows the complete inference rule when applied to any search algorithm. 24) Which of the following option is used to build complex sentences in knowledge representation?
Answer: Explanation: Complex sentences are built by combining the atomic sentences using connectives. 25) Automatic Reasoning tool is used in_____.
Answer: c. LISP Machine Explanation: ART or Automatic Reasoning tool is used in LISP machines to understand the different aspects of reasoning. 26) If according to the hypothesis, the result should be positive, but in fact it is negative, then it is known as_______.
Answer: b. False Positive Hypothesis Explanation: The False Positive Hypothesis means that according to results, you have that condition, but in reality, you don't have it. Such as for a medical test, if someone is found Positive for a disease, but actually he doesn't have that disease, then it comes under the False Positive hypothesis. 27) A hybrid Bayesian Network consist_____.
Answer: c. Both Discrete and Continuous Variables Explanation: The Hybrid Bayesian network contains both discrete and continuous variables as the numerical inputs. To define the hybrid network, both kinds of distributions are used at wide probability distribution. 28) The process of capturing the inference process as Single Inference Rule is known as:
Answer: c. Generalized Modus Ponens Explanation: For all inference process in FOL, the single inference rule can be used, which is called Generalized Modus Ponens. It is said to be the lifted version of Modus ponens. Generalized Modus Ponens can be said as, " P implies Q and P is asserted to be true, therefore Q must be True." 29) Which process makes two different Logical expressions look identical?
Answer: a. Unification Explanation: Unification is the process of making two different logical expressions identical by finding a substitution. 30) Which algorithm takes two sentences as input and returns a Unifier?
Answer: c. Unify Algorithm Explanation: The unify algorithm takes two atomic sentences and return a unifier. It is used for the unification process. 31) The PEAS in the task environment is about____________.
Answer: b. Performance, Environment, Actuators, Sensors Explanation: PEAS is a representation model on which an AI agent works. It is made up of four words:
32) In state-space, the set of actions for a given problem is expressed by the_____.
Answer: b. Successor function that takes current action and returns next state Explanation: The successor function provides a description of all possible actions and their next states, which means their outcomes. 33) In which search problem, to find the shortest path, each city must be visited once only?
Answer: d. Travelling Salesman problem Explanation: The TSP or Travelling Salesman problem is about finding the shortest possible route to visit each city only once and returning to the origin city when the list of all cities and distances between each pair of cities is given. 34) In the TSP problem of n cities, the time taken for traversing all cities, without having prior knowledge of the length of the minimum tour will be_______.
Answer: c. O(n!) Explanation: In the TSP problem of n cities, the time taken for traversing all cities without having prior knowledge of the length of the minimum tour will be O(n!). 35) Web Crawler is an example of______.
Answer: Intelligent Agent Explanation: The web crawler is an example of Intelligent agents, which is responsible for collecting resources from the Web, such as HTML documents, images, text files, etc. 36) The main function of problem-solving agent is to________.
Answer: Both a & b Explanation: Problem-solving agents are the goal-based agents that use different search strategies and algorithms to solve a given problem. 37) In artificial Intelligence, knowledge can be represented as_______. i. Predicate Logic ii. Propositional Logic iii. Compound Logic iv. Machine Logic
Answer: a. Both I and II Explanation: There are several techniques of Knowledge representation in AI, and among them, one is Logical Representation. The logical representation can be done in two ways Predicate Logic and Propositional Logic, hence knowledge can be represented as both predicate and Propositional logic. 38) For propositional Logic, which statement is false?
Answer: a. The sentences of Propositional logic can have answers other than True or False Explanation: Propositional Knowledge or PL is the simplest form of logic that is used to represent the knowledge, where all the sentences are propositions. In this, each sentence is a declarative sentence that can only be either true or False. Such as, It is Sunday today. This sentence can be either true or false only. 39) First order logic Statements contains______.
Answer: c. Predicate and Subject Explanation: The first-order logic is also known as the First-order predicate logic, which is another way of knowledge representation. The FOL statements contain two parts that are subject and Predicate. For e.g., X is an Integer; In this, X is Subject and Is an Integer is Predicate. 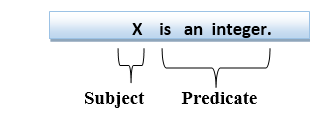 40) A knowledge-based agent can be defined with _____ levels.
Answer: b. 3 Levels Explanation: The knowledge-based agents have the capability of making decisions and reasoning to act efficiently. It can be viewed at three different levels, which are:
41) Ways to achieve AI in real-life are_________.
Answer: c. Both a &b Explanation: Machine Learning and Deep Learning are the two ways to achieve AI in real life. 42) The main tasks of an AI agent are_______.
Answer: c. Perceiving, thinking, and acting on the environment Explanation: The AI agent is the rational agent that runs in the cycle of Perceive, think, and act. 43) The probabilistic reasoning depends upon____________.
Answer: d. All of the above Explanation: The probabilistic reasoning is used to represent uncertain knowledge, where we are not sure about the predicates. It depends Upon Estimation, Observation, and likelihood of objects. 44) The inference engine works on ______.
Answer: c. Both a and b Explanation: The inference engine is the component of the intelligent system in artificial intelligence, which applies logical rules to the knowledge base to infer new information from known facts. The first inference engine was part of the expert system. Inference engine commonly proceeds in two modes, which are:
45) Which of the given statement is true for Conditional Probability?
Answer: c. Conditional Probability has no effect or relevance on independent events. Explanation: The conditional probability is said as the probability of occurring an event when another event has already occurred. And Independent events are those that are not affected by the occurrence of other events; hence conditional probability has no effect or relevance on independents events. 46) After applying conditional Probability to a given problem, we get______
Answer: b. Estimated Values Explanation: Like all probability theories and methods, Conditional Probability also provides the estimated result value, which means the probability of an event to occur, not a 100% accurate result. 47) The best AI agent is one which____________
Answer: b. Can solve a problem on its own without any human intervention Explanation: The best AI agent is one that can solve the problem on its own without any human intervention. 48) The Bayesian Network gives________
Answer: c. A complete description of the domain Explanation: A Bayesian network is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies using a directed acyclic graph. It gives a complete description of the domain. 49) In LISP, the addition of 5+8 is entered as_______.
Answer: d. (+5 8) Explanation: The sum of two variables a & b can be entered as (+a b). Hence the sum of 5 and 8 can be entered as (+5 8). 50) An Algorithm is said as Complete algorithm if_______________
Answer: a. It ends with a solution (if any exists). Explanation: An algorithm is only said the complete algorithm if it ends with a solution (if it exists). 51) Which statement is valid for the Heuristic function?
Answer: d. The heuristic function calculates the cost of an optimal path between the pair of states Explanation: The heuristic function is used in Informed search in AI to find the most promising path in the search. It estimates the closeness of the current state and calculates the cost of an optimal path between the pair of states. It is represented by h(n). 52) Which of the given element improve the performance of AI agent so that it can make better decisions?
Answer: c. Learning Element Explanation: The learning element improves the performance of an AI agent while solving a given problem, so that it can make better decisions. 53) How many types of Machine Learning are there?
Answer: c. 3 Explanation: There are three types of Machine Learning techniques, which are Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. 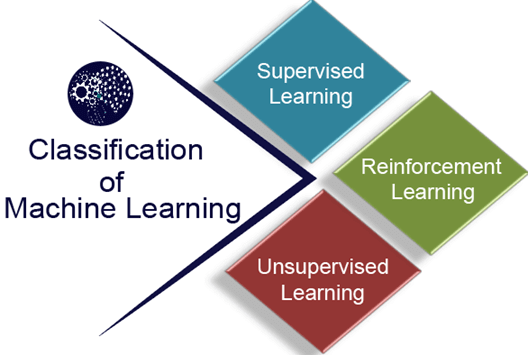 54) The decision tree algorithm reaches its destination using_____________.
Answer: c. Sequence of test Explanation: A decision tree is the supervised machine learning technique that can be used for both Classification and Regression problems. It reaches its destination using a Sequence of Tests. 55) In LISP programming, the square root is entered as_____.
Answer: (sqrt x) Explanation: In LISP programming, the square root of any variable x is entered as (sqrt x). Next TopicAI Tutorial |