Amazon CloudFrontAmazon CloudFront is a fast content delivery network (CDN) service that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers globally with low latency, high transfer speeds, all within a developer-friendly environment. CloudFront China has Edge locations in Beijing, Shanghai, Zhongwei, and Shenzhen. These four Edge locations are connected by private network directly to Amazon Web Services China (Beijing) Region operated by Sinnet and Amazon Web Services China (Ningxia) Region operated by NWCD for speedy content delivery to viewers in China. CloudFront works seamlessly with services, including Amazon Shield Standard for DDoS mitigation, Amazon S3, Elastic Load Balancing, or Amazon EC2 as origins for your applications. You can get started with the Content Delivery Network in minutes, using the Amazon Web Services tools you're already familiar with: APIs, Amazon Web Services Management Console, Command Line Interface (CLI), and SDKs. Amazon's CDN offers a simple, pay-as-you-go pricing model with no upfront fees or required long-term contracts, and support for the CDN is included in your existing Amazon Support subscription. BenefitsFast and global The Amazon CloudFront content delivery network (CDN) is massively scaled and globally distributed. The CloudFront network has 191 POPs (180 edge locations and 11 Regional Edge Caches) in 73 cities across 33 countries. It leverages the highly-resilient private backbone network for superior performance and availability for your end-users. Security at the Edge Amazon CloudFront is a highly-secure CDN that provides network and application-level protection. Your traffic and applications benefit through various built-in protections such as Amazon Shield Standard at no additional cost. Deep integration with Amazon Web Services Amazon CloudFront China is integrated with Amazon Web Services services such as Amazon S3, Amazon EC2, and Elastic Load Balancing. They are all accessible via the same console, and all features in the CDN can be programmatically configured by using SDKs or the Amazon Web Services Management Console. Lastly, if you use Amazon Web Services origins such as Amazon S3, Amazon EC2, or Elastic Load Balancing, you don't pay for any data transferred between these services and CloudFront. Amazon Cloud Front edge locationsIn October 2018, Amazon CloudFront consisted of 138 access points (127 edge locations and 11 regional edge caches) in 63 cities across 29 countries.[4] North AmericaEdge locations: Ashburn, VA (3); Atlanta, GA (3); Boston, MA; Chicago, IL (2); Dallas/Fort Worth, TX (5); Denver, CO (2); Hayward, CA; Jacksonville, FL; Los Angeles, CA (4); Miami, FL (3); Minneapolis, MN; Montreal, QC; New York, NY (3); Newark, NJ (3); Palo Alto, CA; Philadelphia, PA; Phoenix, AZ; San Jose, CA (2); Seattle, WA (3); South Bend, IN; St. Louis, MO; Toronto, ON Regional Edge caches: Virginia; Ohio; Oregon EuropeEdge locations: Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2); Berlin, Germany; Copenhagen, Denmark; Dublin, Ireland; Frankfurt, Germany (8); Helsinki, Finland; London, England (7); Madrid, Spain (2); Manchester, England; Marseille, France; Milan, Italy; Munich, Germany; Oslo, Norway; Palermo, Italy; Paris, France (4); Prague, Czech Republic; Stockholm, Sweden (3); Vienna, Austria; Warsaw, Poland; Zurich, Switzerland Regional Edge caches: Frankfurt, Germany; London, England AsiaEdge locations: Bangalore, India; Chennai, India (3); Bangkok, Thailand (2); Hong Kong, China (3); Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; Mumbai, India (2); Manila, Philippines; New Delhi, India (2); Osaka, Japan; Seoul, South Korea (4); Singapore (3); Taipei, Taiwan(3); Tokyo, Japan (9) Regional Edge caches: Mumbai, India; Singapore; Seoul, South Korea; Tokyo, Japan AustraliaEdge locations: Melbourne; Perth; Sydney Regional Edge caches: Sydney South AmericaEdge locations: São Paulo, Brazil (2); Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (2) Regional Edge caches: São Paulo, Brazil Middle EastEdge location: Dubai, United Arab Emirates; Fujairah, United Arab Emirates; Tel Aviv, Israel AfricaEdge locations: Nairobi, Kenya; Johannesburg, South Africa; Cape Town, South Africa How do you set up CloudFront to deliver content?You create a CloudFront distribution to tell CloudFront where you want the content delivered and details about how to track and manage the content delivery. CloudFront then uses computer-edge servers-closer to your audience-to quickly deliver that content when someone wants to view or use it. 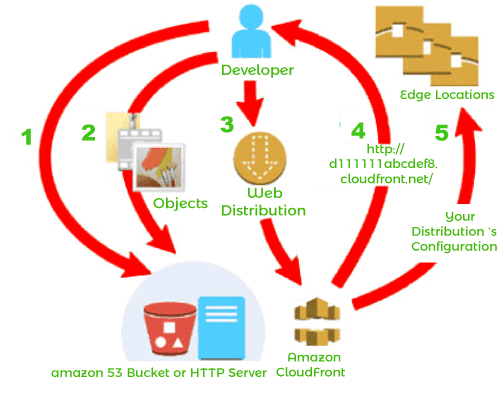 How do you configure Cloud Front to deliver your content1. You specify the origin server, such as Amazon S3 Bucket or your HTTP server, from which CloudFront gets your files, which will then be distributed from CloudFront edge locations around the world. An origin server stores the original, fixed version of your items. If you're serving content over HTTP, your origin server is either an Amazon S3 bucket or an HTTP server, such as a web server. Your HTTP server may be running on an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance or a server you manage; These servers are also known as custom origins. 2. You upload your files to your origin server. Your files, also known as objects, typically include web pages, images, and media files but can also be anything that can be served over HTTP. If you're using an Amazon S3 bucket as the origin server, you can make the objects in your bucket publicly readable so that anyone who knows the CloudFront URL for your items can access them. You also can keep objects private and control who has access to them. You create a CloudFront distribution, which tells CloudFront which origin server to get your files from when users request files through your website or application. At the same time, you specify whether you want CloudFront to log all requests and whether you want it to be enabled as soon as the distribution is built. 3. CloudFront specifies a domain name for your new distribution that you can view in the CloudFront console or return in response to a programmatic request, such as an API request. If you wish, you can add an alternate domain name to use instead. 4. CloudFront sends your distribution's configuration (but not your content) to all of its edge locationsor points of presence (POPs) - collections of servers in geographically dispersed data centers where CloudFront caches copies of your files. You use CloudFront's domain name for your URL as you develop your website or application. For example, if CloudFront returns d111111abcdef8.cloudfront.net as the domain name for your distribution, the URL for logo.jpg in your Amazon S3 bucket (or in the root directory on the HTTP server) is http://d111111abcdef8. is CloudFront. net/logo.jpg. Or you can set up CloudFront to use your domain name with your distribution. In that case, the URL might be http://www.example.com/logo.jpg. CloudFront use casesUsing CloudFront can help you achieve a variety of goals. This section lists just a few with links to more information to give you an idea of the possibilities. Accelerate static website content deliveryCloudFront can accelerate the delivery of your static content (for example, images, style sheets, JavaScript, and so on) to audiences around the world. Using CloudFront, you can take advantage of the AWS backbone network and CloudFront Edge servers to provide a fast, secure, and reliable experience for your visitors when they visit your website. A simple way to store and distribute static content is to use an Amazon S3 bucket. There are many benefits to using S3 with CloudFront, including the option to use Origin Access Identity (OAI) to restrict access to your S3 content easily. Next TopicGoals of Artificial Intelligence |